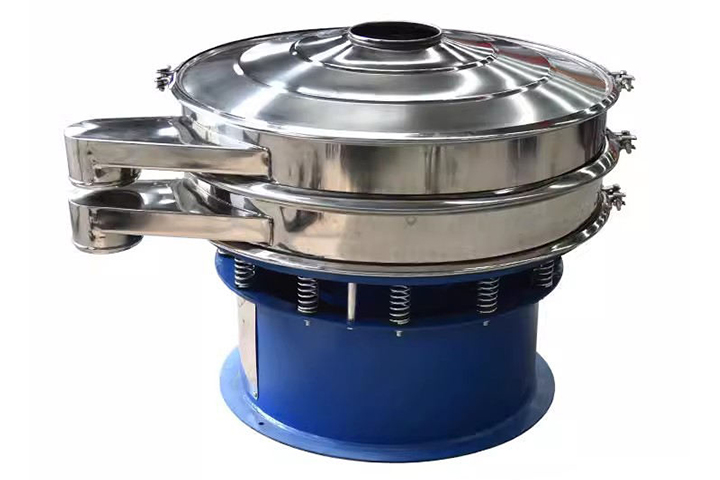
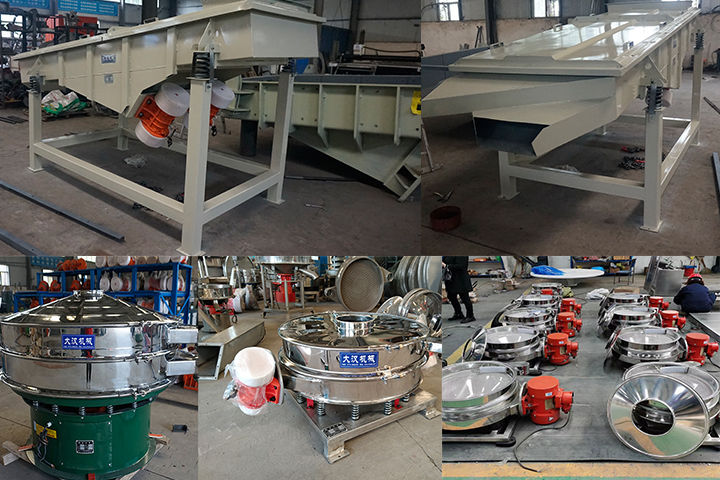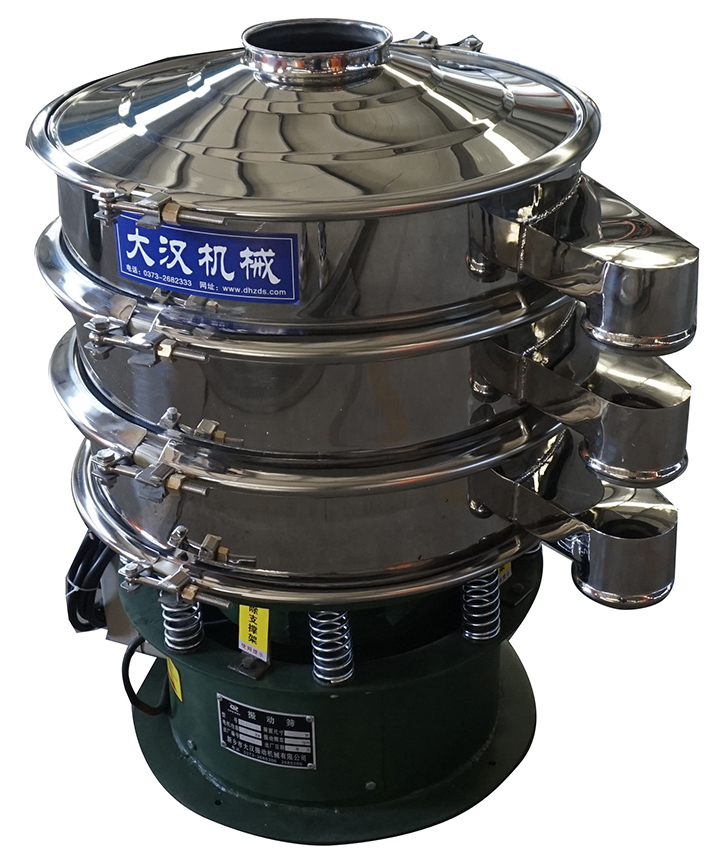
Industrial Sieving Machine
An industrial sieving machine is a mechanical device used for screening, filtering, and grading materials. It is widely used in various industries, including chemicals, food, pharmaceuticals, mining, and building materials. Its primary function is to separate materials of varying particle sizes, ensuring product quality and production efficiency. Operating Temperature: -20°C to 100°C (customizable with refractory materials) Mounting Angle: ≤20° Material: Carbon steel, stainless steel, etc. Types: Vibrating, drum, etc.
What is an industrial sieving machine?
An industrial sieving machine uses the relative motion between the screen surface and the material to separate granular or powdered materials into different grades based on particle size. With its superior performance and diverse range of options, industrial screens can precisely adapt to the challenges of the material screening process, enabling material grading, purification, or separation. This improves screening efficiency while maintaining precise screening accuracy. It is a key piece of equipment in material pretreatment, processing, and purification processes during industrial production.
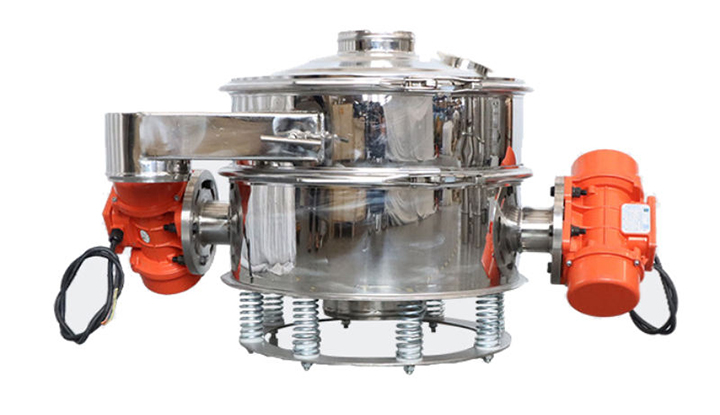

How does an industrial sieving machine work?
Industrial sieving machine use a power device (such as a motor) to generate a specific motion (commonly vibration, reciprocating oscillation, or rotation), causing the material to bounce, slide, or tumble across the screen surface. As the material moves, particles smaller than the screen hole diameter pass through the screen holes, becoming the undersize material. Particles larger than the screen hole diameter remain on the screen surface, becoming the oversize material, thus achieving material separation and grading.
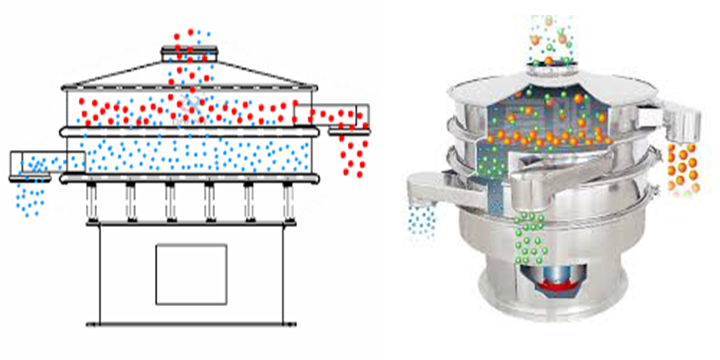
What is the structure of an industrial sieving machine?
Screen box: Holds the screen mesh and material.
Screen frame: Maintains the flatness of the screen mesh, ensuring proper screening.
Screen mesh: A key component for screening, available in a variety of mesh sizes.
Vibrator: The motor drives the eccentric block to rotate, generating centrifugal inertia, forcing the screen box to vibrate.
Vibration damping springs: Reduce the negative impact of vibration on the machine and its surroundings.
Support: Supports the equipment and ensures stable operation of the screen.
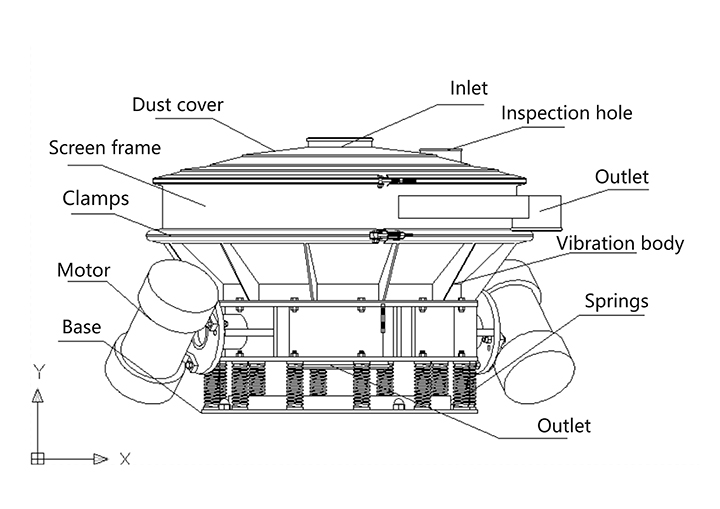
What are the parameters of an industrial sieving machine?
Industrial screen models:
| 模型 |
直径 (毫米) |
进料尺寸 (mm) |
频率 (转/分) |
图层 |
功率 (千瓦) |
产量 (公斤/小时) |
| DH-400 | 400 | <10 | <1500 | 1-5 | 0.18 | 100 |
| DH-600 | 600 | 0.25 | 200 | |||
| DH-800 | 800 | 0.55 | 500 | |||
| DH-1000 | 1000 | 0.75 | 800 | |||
| DH-1200 | 1200 | 1.1 | 1200 | |||
| DH-1500 | 1500 | 1.5 | 1800 | |||
| DH-1800 | 1800 | 2.2 | 2000 |
Material handling of industrial screens:
Types and advantages of industrial sieving machine?
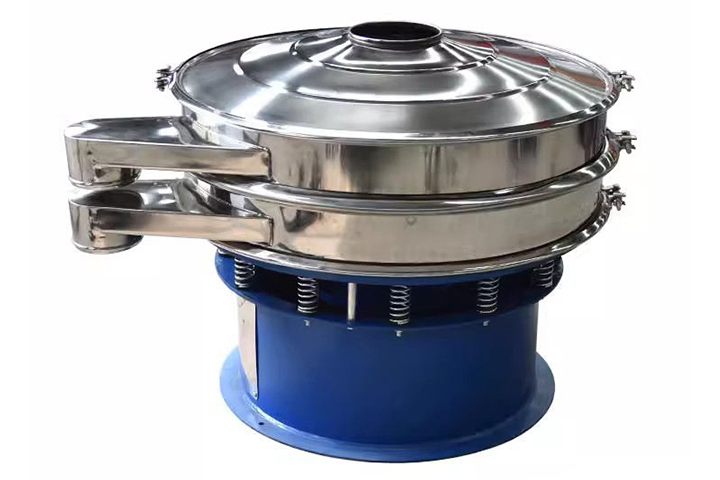
Vibrating screens: A motor drives an eccentric block to generate high-frequency vibration (small amplitude, high frequency), causing the material to be tossed or slid across the screen surface. This results in high screening efficiency (over 85%) and a large processing capacity. They can be further categorized into linear and circular vibrating screens. They are the most widely used.
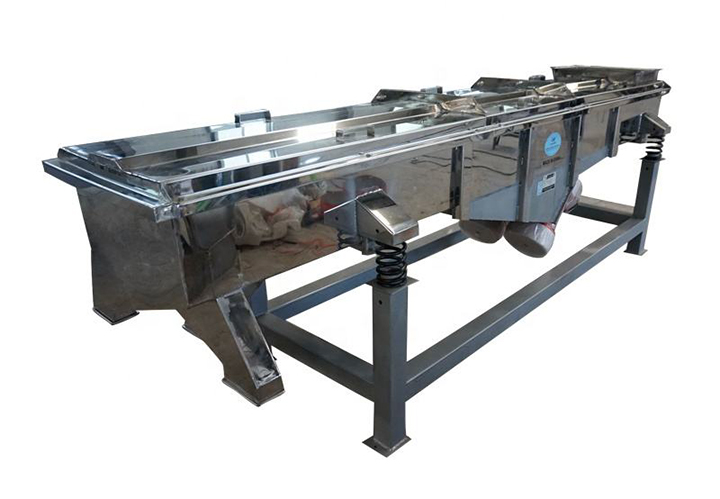

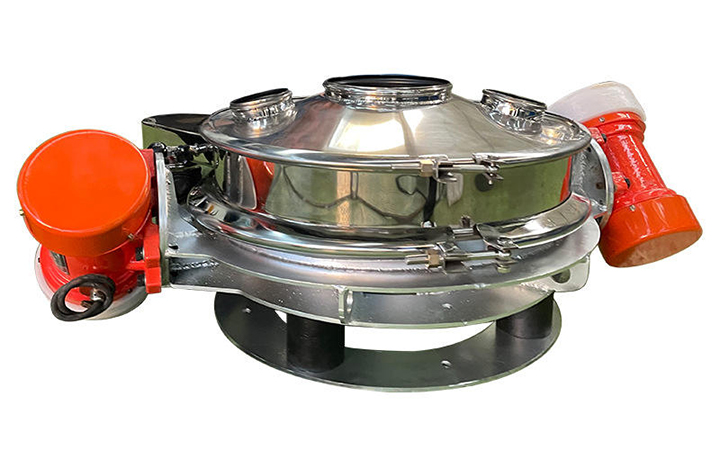
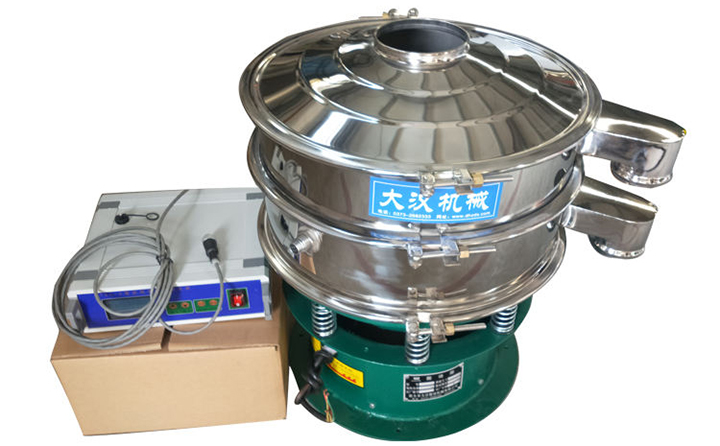
Rotary vibrating screens: The unique three-dimensional vibration path (horizontal, vertical, and inclined composite motion) of a rotary vibrating screen allows for higher screening accuracy and a wider range of material applications. Its fully enclosed structure meets the high hygiene requirements of industries such as food and pharmaceuticals.
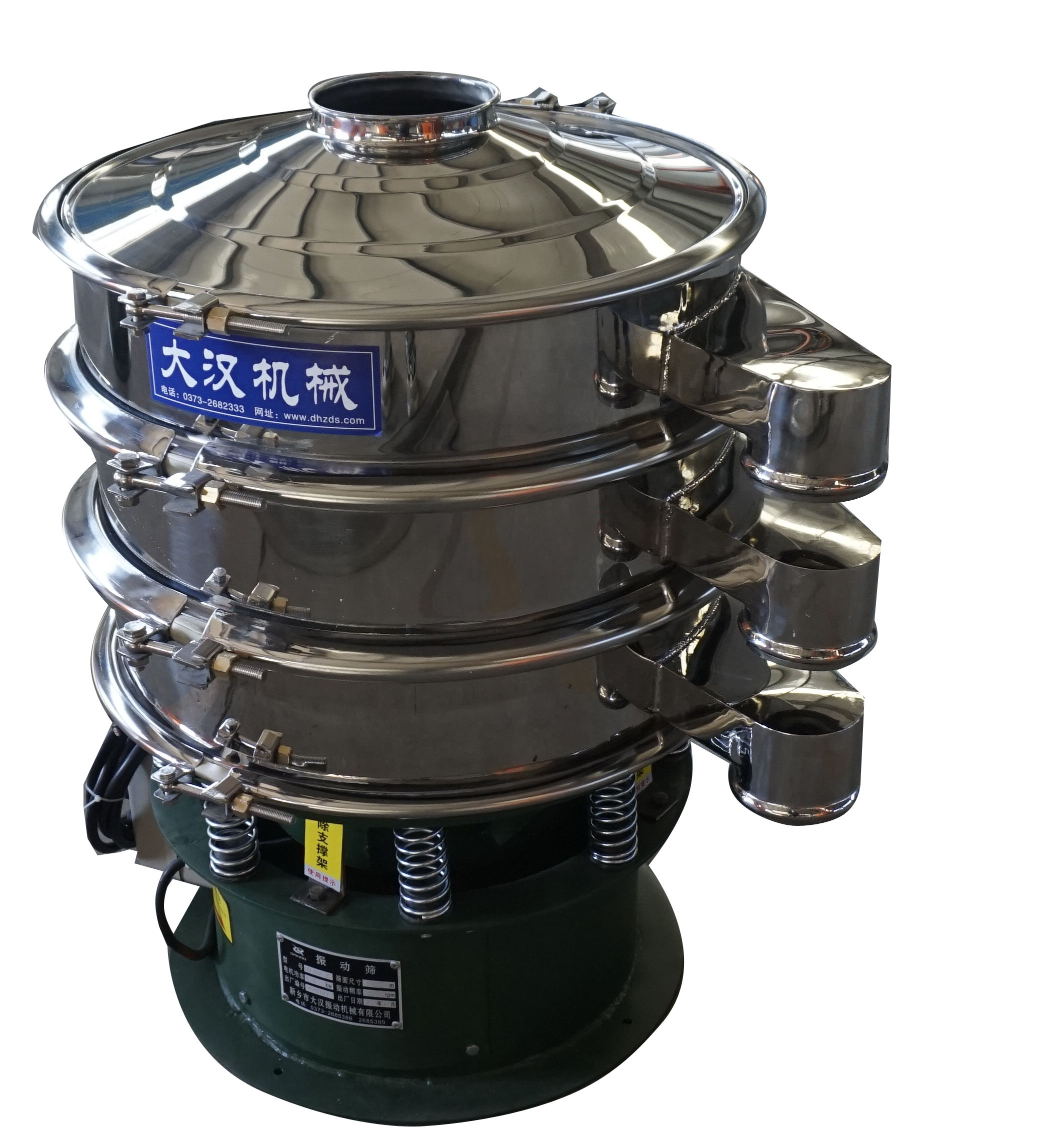

Swing screens: Simulating the swing path of manual screening (combined forward and backward, left and right motions), the material slides slowly across the screen surface, extending the screening time and providing high screening accuracy (over 95%), but with a lower processing capacity. They minimize material damage and are suitable for fragile materials (such as nuts and plastic pellets). They also provide fine screening and can process highly viscous or easily agglomerated materials. They are commonly used in the food and light industries.
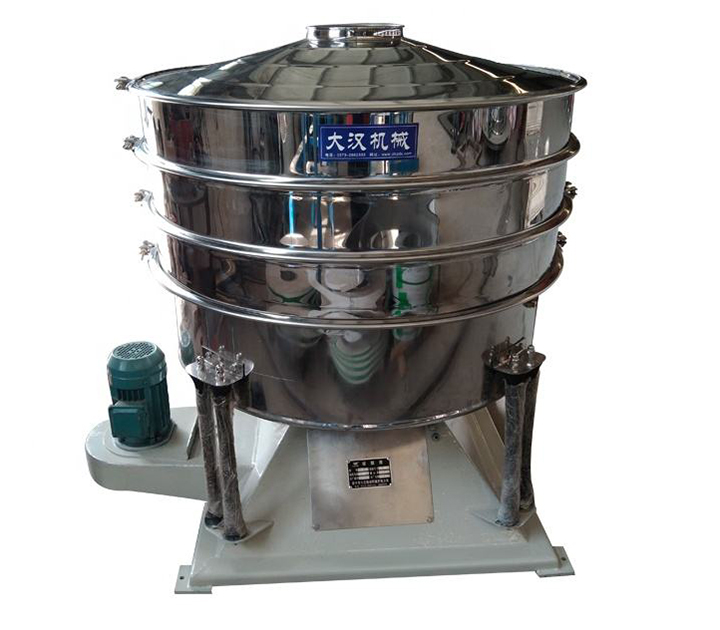

Ultrasonic screening: Superimposing ultrasonic vibrations on vibrations effectively eliminates the problem of fine powders clogging the sieve apertures. It offers extremely high screening accuracy (capable of processing micron-sized materials) and is suitable for processing ultrafine powder materials (such as nanomaterials and battery materials).

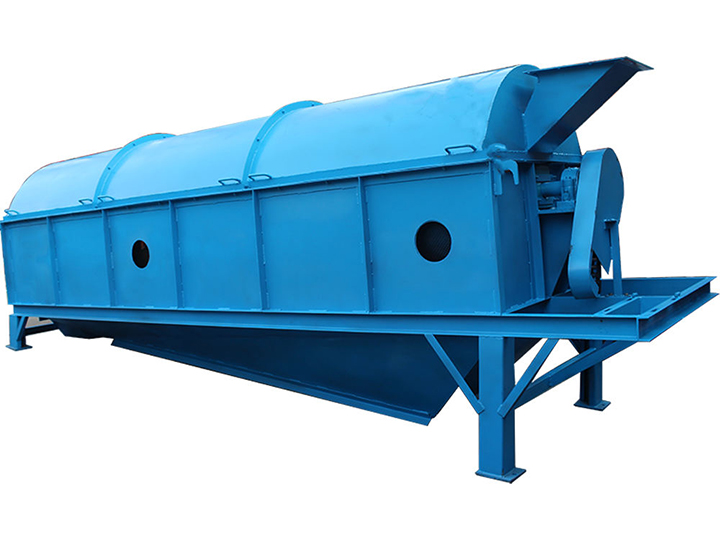
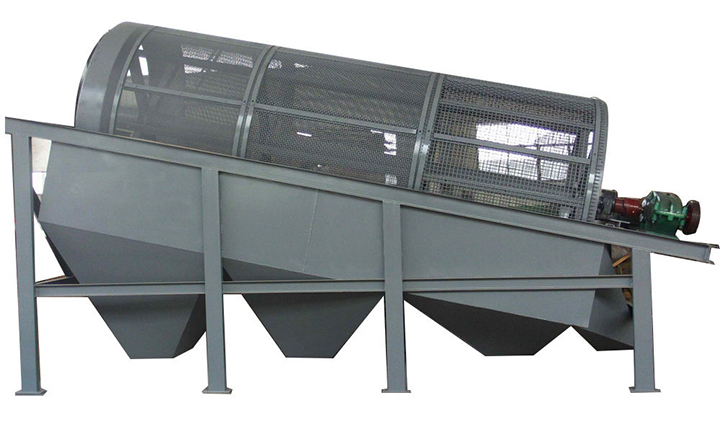
Drum screening: The working part is cylindrical, and the entire sieve rotates around the cylinder's axis. Material enters at one end and exits at the other, achieving screening during the rotation. It is suitable for screening wet, sticky materials or applications where screening efficiency is not a priority.

What are the applications of industrial sieving machine?
Mining and metallurgy: Screening, grading, and removing impurities from ore to provide qualified raw materials for subsequent processes.
Building materials and road industry: Screening and grading ore, cement, and lime, as well as recycling construction waste.
Food and pharmaceutical industry: Screening or removing impurities from flour, nuts, fruits and vegetables, medicinal powders, and granules.
Chemical industry: Screening, grading, or removing impurities from chemical raw materials and products.
Agriculture and grain processing: Screening seeds, removing impurities from grains, and grading fruit and tea.
As well as screening, grading and impurity removal processes in other industries to improve product quality and production efficiency.






