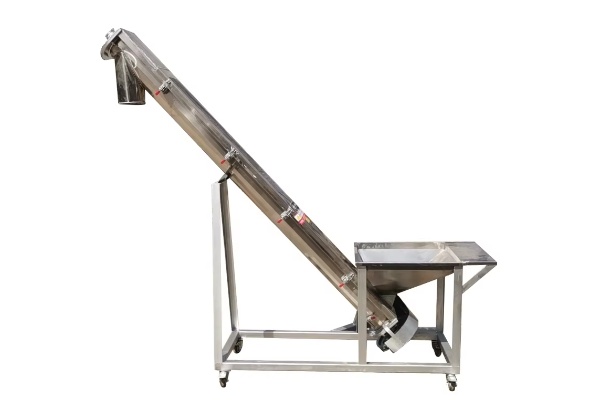
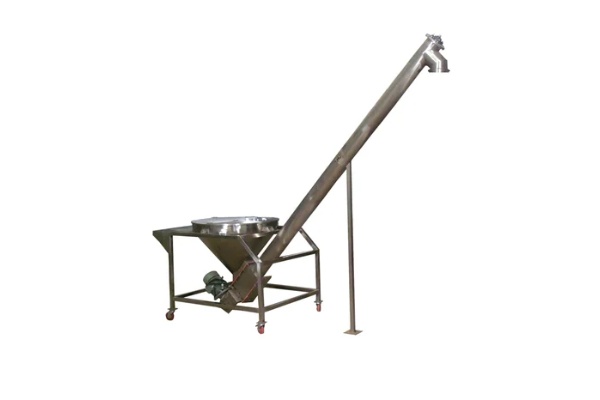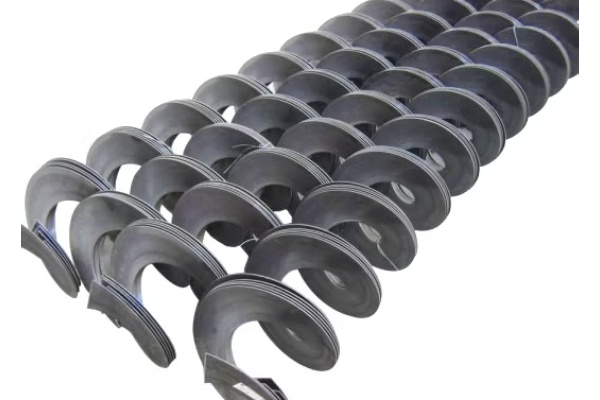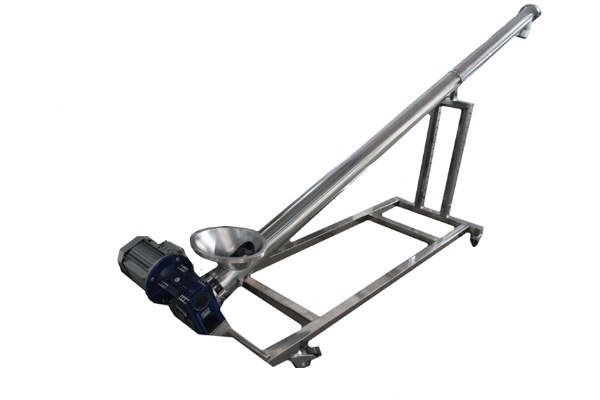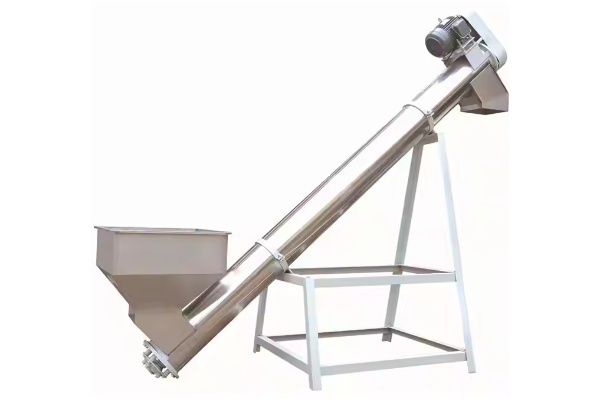
Screw Feeder
The price of Screw Feeder varies from $100 to $6,500, depending on factors such as model, material, processing capacity, brand and customization requirements.
Voltage: 220V, 380V
Power: 1kW, 2KW, 3KW, 5KW
Productivity: 500L/hour
Size: 1500mm L * 200mmW/customized
Rotation speed: 45-70 R/Min
Material: Stainless steel/Carbon steel/Plastic
What is a Screw Feeder?
Screw Feeder is a common material conveying equipment that mainly uses rotating spiral blades to continuously feed or quantitatively convey bulk materials along a closed trough. There are many types of this type of feeder, including horizontal Screw Feeder, U-shaped Screw Feeder, tubular Screw Feeder and shaftless Screw Feeder, depending on different application scenarios and material characteristics. Screw Feeder has a wide range of processing capabilities, with small ones being able to convey several kilograms of material per hour and large ones being able to reach hundreds of tons per hour. The conveying distance is usually within tens of meters, which makes it suitable for short-distance material transmission conditions with high airtightness requirements.
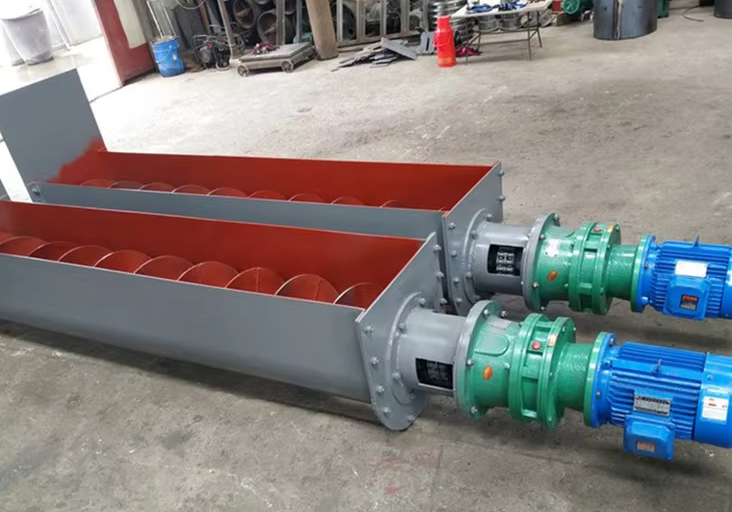
Screw Feeder is a common material conveying equipment in industrial production, and its various types enable it to adapt to various working conditions. According to the conveying direction, Screw Feeder can be divided into horizontal, inclined and vertical types. The horizontal type is mainly used for short-distance horizontal conveying; the inclined type is suitable for material lifting at a certain angle; the vertical type can achieve vertical lifting of materials, especially suitable for occasions with limited space. According to the structural material, the common types are carbon steel, stainless steel and special alloy. According to the trough and spiral structure, it can be divided into U-shaped trough and round tube. Choosing the right type of Screw Feeder can significantly improve production efficiency.

What are the types of Screw Feeders?
Screw Feeders, as a common bulk material conveying equipment, can be divided into multiple types according to different classification standards. These types differ in structure, applicable materials and application scenarios.
Classification by conveying direction
Horizontal Screw FeederFeatures: The material is pushed forward by the rotation of the spiral blades in a horizontally placed trough or tube. Its structure is relatively simple, and the manufacturing and maintenance costs are usually low.
Conveying distance: It is suitable for medium and short distance material conveying, and the length of a single machine can usually reach tens of meters. Longer distances may require multi-stage series connection or other conveying equipment.
Conveying capacity: Among the three types, the conveying capacity of the horizontal Screw Feeder is usually larger because it has a relatively high efficiency in stacking and pushing materials in the horizontal direction. The conveying capacity is related to the screw diameter, pitch, speed and material characteristics.
Inclined Screw FeederFeatures: The inclined Screw Feeder is based on the horizontal direction, and the fuselage is tilted upward at a certain angle. This design allows materials to be lifted to a higher height, saving space and reducing the need for other lifting equipment.
Conveying distance: The conveying distance is usually shorter than the horizontal type because it needs to overcome the gravity of the material and the lifting height is also limited.
Conveying capacity: Compared with the horizontal Screw Feeder, the conveying capacity of the inclined Screw Feeder is usually slightly lower at the same screw diameter and speed. This is because when the material moves obliquely upward, it will be affected by the gravity component, and some materials may have backflow.
Incline angle: The general inclination angle can be between 20° and 45°.
Vertical Screw FeederFeatures: The vertical Screw Feeder lifts the material vertically upward. This type usually uses a high-speed rotating shaftless screw or a high-speed screw in a tubular housing to lift the material through centrifugal force or the strong push of the screw. The structure is compact and occupies a small area.
Conveying distance: It is suitable for lifting materials in the vertical direction, and the conveying height can reach several meters or even higher.
Conveying capacity: The conveying capacity of the vertical Screw Feeder is greatly affected by the material characteristics and the screw speed. Because it needs to overcome all gravity, its conveying capacity is usually lower than that of the horizontal and inclined types at the same diameter.

Classification by structural material
Carbon steel screw feederFeatures: Carbon steel is a common structural material with good strength and processing performance. The cost is relatively low. The surface can be treated with anti-corrosion such as painting and galvanizing.
Applicable materials: Suitable for conveying bulk materials that are generally non-corrosive and have no special hygiene requirements, such as coal, ore, cement, sand, grain, etc.
Stainless steel screw feederFeatures: Stainless steel has good corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance and hygienic properties. The surface is smooth, not easy to adhere to materials, and easy to clean. It is divided into a variety of grades (such as 304, 316L, etc.) to adapt to different degrees of corrosion.
Applicable materials: Widely used in industries with high requirements for hygiene and anti-corrosion, such as food, chemical industry (specific corrosive media), fine chemicals, etc. It can convey flour, starch, sugar, chemical additives, etc.
Plastic screw feederFeatures: It mainly refers to the spiral blades or some parts that contact the material are made of engineering plastics. Plastics have the characteristics of corrosion resistance, self-lubrication, wear resistance (specific plastics), and light weight.
Applicable materials: Suitable for conveying corrosive, sticky, or metal-abrasive materials, such as certain chemicals, wet sludge, specific food additives, etc. It is also used in some occasions where metal contamination needs to be avoided.

Classification by trough body and spiral structure
U-type Screw FeederFeatures of U-type shafted Screw Feeder: The spiral blades are welded or fixed on the central shaft, and the materials are pushed by the rotation of the shaft. The structure is strong, the support point is clear, and the operation is stable. The existence of the central shaft may cause the material to entangle or bridge during the conveying process, especially for fibrous and viscous materials. Suitable for medium and long-distance horizontal or small-angle conveying. Suitable for most conventional powdery, granular and some small block materials, such as cement, fly ash, grain, sand, etc. Not suitable for sticky materials that are easy to entangle or have a high moisture content.
Features of U-type shaftless Screw Feeder: The spiral body has no central shaft, only a thick spiral blade (usually high-strength wear-resistant steel or stainless steel), which is supported by the liner to slide in the U-shaped trough. This design effectively avoids the problem of material entanglement and blockage, and is especially suitable for the transportation of sticky, easy-to-entangle or blocky materials. Cleaning is relatively convenient. Suitable for medium and short distance transportation, especially when special materials need to be handled. Mainly used for conveying sticky materials (such as sludge, wet garbage), entangled materials (such as fiber, straw), bulk materials and waste from some special industries.
Tubular Screw FeederFeatures: The spiral blades are installed in a circular tubular shell. This structure has good sealing, which can effectively prevent dust leakage and material moisture and contamination, and also avoid contact between materials and the external environment. At the same time, the tubular structure occupies little space and can be arranged at multiple angles.
Applicable materials: Mainly used for conveying powdery and granular dry materials, such as cement, flour, chemical powder, grains, etc., especially suitable for occasions that require closed transportation, dust prevention, moisture prevention or avoidance of material contamination.
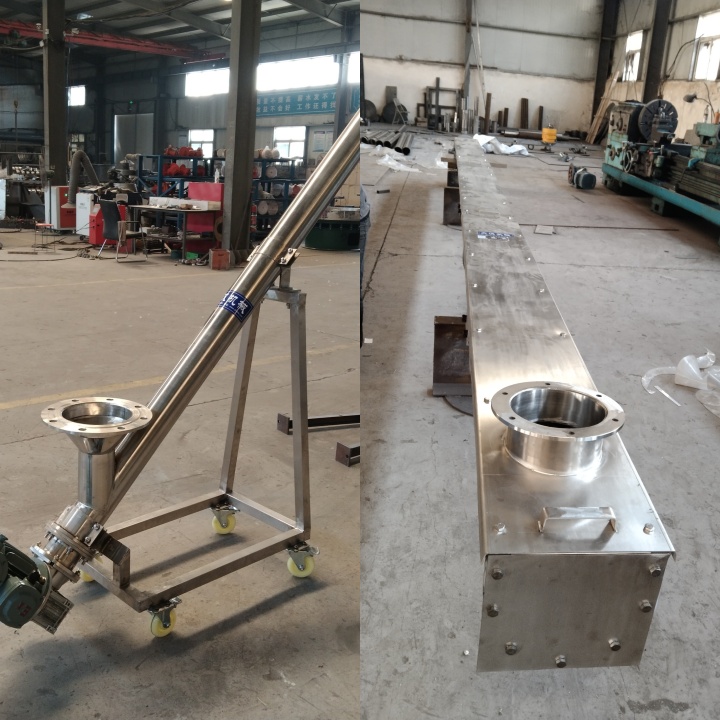

What are the advantages of Screw Feeder?
As an important material handling equipment, Screw Feeder has the following significant advantages compared with other feeding and conveying methods:
Accurate and uniform feeding capacity: By accurately controlling the speed of the screw (especially through frequency conversion speed regulation), the material conveying amount can be accurately controlled and continuously and evenly supplied.
Wide adaptability: It can handle various forms of bulk materials, including powder, granular, and small block materials. For special materials such as poor fluidity, easy bridging, high viscosity, high moisture content, and easy winding (shaftless type), reliable feeding can be achieved by selecting the appropriate spiral blade type (such as variable pitch, conical, paddle type) or adopting a shaftless design.
Flexible conveying direction: It can achieve horizontal and inclined conveying, and even vertical lifting under certain specific designs to adapt to different process layouts and space restrictions.
Compact structure and small footprint: Compared with belt feeders or vibrating feeders, Screw Feeders usually have a smaller cross-sectional area and a more compact overall structure. This makes them more flexible in installation and layout within limited production space.
Material mixing and stirring function (some types): Some specially designed spiral blades (such as paddle blades and segmented blades) can not only convey materials, but also play a certain role in stirring, mixing or breaking up lumps, thus achieving multiple uses of one machine.

Basic parameters of Screw Feeder
| Model |
Diameter (mm) |
Pitch (mm) |
Rotating speed (r/min) |
Capacity (m³/h) |
Rotating speed (r/min) |
Capacity (m³/h) |
Rotating speed (r/min) |
Capacity (m³/h) |
Rotating speed (r/min) |
Capacity (m³/h) |
|
| Small | 100 | 100 | 100 | 140 | 2.2 | 112 | 1.7 | 90 | 1.4 | 71 | 1.1 |
| 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 3.8 | 100 | 3 | 80 | 2.4 | 63 | 1.9 | |
| 160 | 160 | 160 | 112 | 7.1 | 90 | 5.7 | 71 | 4.5 | 56 | 3.6 | |
| 200 | 200 | 200 | 100 | 12.4 | 80 | 9.9 | 63 | 7.8 | 50 | 6.2 | |
| Small | 250 | 250 | 250 | 90 | 21.8 | 71 | 17.2 | 56 | 13.6 | 45 | 10.9 |
| 315 | 315 | 315 | 80 | 38.8 | 63 | 30.5 | 50 | 24.2 | 40 | 13.4 | |
| 400 | 400 | 355 | 71 | 62.5 | 56 | 49.3 | 45 | 38.6 | 36 | 31.7 | |
| Large | 500 | 500 | 400 | 63 | 97.7 | 50 | 77.6 | 40 | 62 | 32 | 49.6 |
| 630 | 630 | 450 | 50 | 138.5 | 40 | 110.8 | 32 | 88.6 | 25 | 69.3 | |
| 800 | 800 | 500 | 40 | 198.5 | 32 | 158.8 | 25 | 124.1 | 20 | 99.3 | |
What are the applications of Screw Feeder?
Screw Feeder is widely used in multiple industries and material handling scenarios because of its ability to achieve precise, uniform and continuous feeding.
Accurate metering and proportioning of materials: Screw Feeder can stably convey powdered and granular materials to the next link according to the preset amount or speed. This is especially important in scenarios where multiple materials need to be mixed in a specific proportion, ensuring the accuracy of the formula.
Stable feeding of continuous production lines: In automated production lines that require continuous and uninterrupted material flow, Screw Feeder can continuously feed materials from silos or hoppers to subsequent processing equipment, such as reactors, mixers, packaging machines, etc., to ensure the smooth operation of the entire production process.
Handling special materials: For some materials with poor fluidity, easy bridging, high viscosity, high moisture content or easy entanglement, Screw Feeder can also effectively handle them by selecting appropriate spiral blade design (such as shaftless, variable pitch or paddle type) and trough structure to avoid blockage and jamming.
Control environmental pollution: Most Screw Feeders adopt a fully enclosed design, which can effectively prevent dust flying, odor diffusion and material leakage generated during the material transportation process, which helps to improve the working environment and reduce the impact on the surrounding environment.
Transfer and lifting of materials: In addition to precise feeding, Screw Feeder can also undertake horizontal and inclined material transportation tasks. Under certain special designs, it can even achieve vertical lifting, transporting materials from low positions to high positions, adapting to different factory layouts and space restrictions.
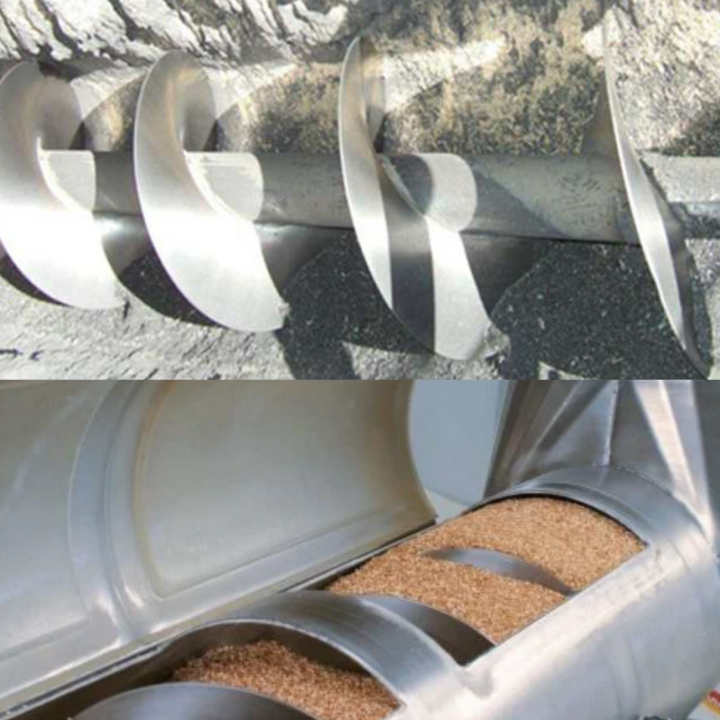

What are the cases of Screw Feeder?
Screw Feeder has demonstrated excellent material conveying capabilities in various industries with its unique structure and working principle. It is mainly composed of spiral blades, U-shaped grooves or round tubes, drive devices and brackets. The rotating spiral blades continuously push the material along the direction of the groove to achieve quantitative or unquantified feeding and conveying. In the chemical industry, Screw Feeder is often used to convey powdered and granular chemical raw materials, additives, catalysts, etc. to ensure the stability of the production process and the accuracy of the material ratio. In the building materials industry, the conveying of bulk materials such as cement, clinker, limestone powder, and coal powder is inseparable from Screw Feeder. Whether it is the raw material pretreatment of cement plants or the aggregate ratio of concrete mixing plants, Screw Feeder can provide a reliable conveying solution to ensure the continuity of production and product quality. In the grain processing industry, Screw Feeder is used to convey agricultural products such as grains, flour, and feed. From grain storage to processing into finished products, Screw Feeder is an important link. In the metallurgical industry, it is widely used in the transportation of high-temperature or abrasive materials such as ore, concentrate powder, sintered materials, coke, etc. In short, Screw Feeder plays a vital role in improving production efficiency and ensuring material transportation quality with its advantages of simple structure, good sealing and easy maintenance, and has become an indispensable transportation equipment in industrial production.
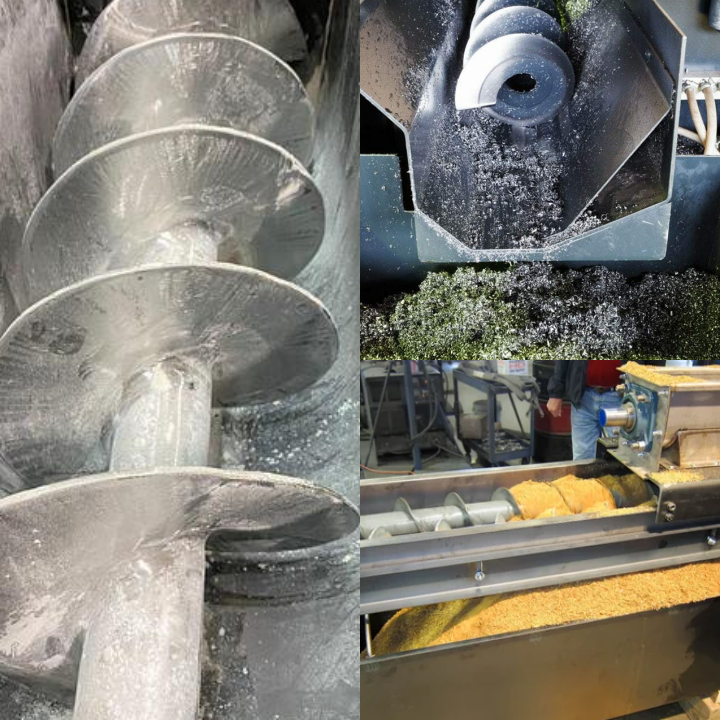

Screw Feeder Manufacturers
Screw Feeder manufacturers show significant differences in product design and customization capabilities. The differences in products are first reflected in the division of standardized models and customized models. Many manufacturers will provide a series of standardized Screw Feeders, which are generally suitable for common materials and working conditions, with the advantages of high cost-effectiveness and short supply cycle. However, for some special applications, such as highly abrasive materials, high temperature environments, strict hygiene requirements, or scenarios that require precise proportions, standardized products may not meet the needs. At this time, the manufacturer's customization capabilities are particularly critical. This capability is reflected in many aspects, such as material selection. In view of the corrosiveness and abrasiveness of different materials, manufacturers can provide a variety of material options such as carbon steel, stainless steel (such as 304, 316L), and various special alloys to ensure the service life of the equipment and the purity of the material. The structural design includes the type of spiral blades (such as continuous, segmented, paddle), pitch, diameter, shell form (U-groove, tubular), and the design of the inlet and outlet. Manufacturers can optimize the design based on the material's fluidity, adhesion, and whether it is easy to form arches, to ensure smooth material transportation. Customization also includes selecting the appropriate motor power, reducer type, and variable frequency speed control system to achieve precise feeding speed control and meet the flow accuracy requirements of different processes. In some cases, an automated control system is also integrated to achieve linkage with other production equipment. In short, the product line of screw feeder manufacturers covers a variety of types from general to highly specialized.
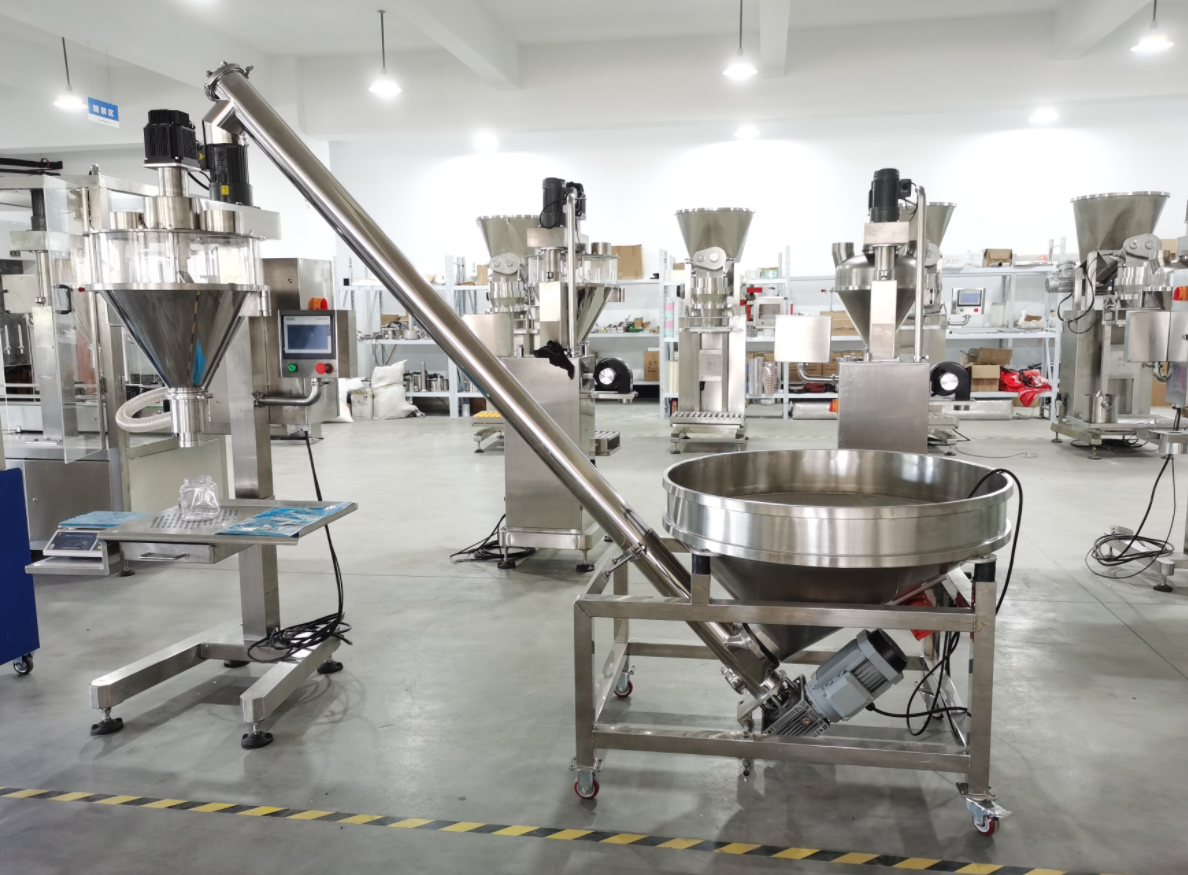

Screw Feeder Price
As a key equipment for material transportation in various industries, the market price of Screw Feeder varies depending on many factors, with a wide price range, ranging from US$100 to US$6,500. The price of Screw Feeder is affected by many factors, among which the material is the primary consideration. Commonly used carbon steel has a lower cost, while corrosion-resistant stainless steel (such as 304, 316L) is more expensive, and special alloy steel is even more expensive. Secondly, the specifications and processing capacity of the equipment directly determine the cost. The larger the diameter of the spiral blade, the pitch, the conveying length, and the motor power, the higher the required material and manufacturing costs. Therefore, the equipment with stronger processing capacity has a higher price. In addition, the function and configuration of the Screw Feeder are also important factors. Whether special functions such as frequency conversion speed regulation, weighing and metering, heating or cooling jackets, anti-blocking devices, and cleaning devices are required will significantly increase the complexity and cost of the equipment. The degree of automation also has a great impact on the price. Manually controlled equipment is cheaper, while equipment with highly automated functions such as PLC control and remote monitoring will significantly increase the cost of the control system. Brand and technology are also key factors in determining price. In summary, when purchasing a screw feeder, it is recommended to communicate in detail with multiple suppliers based on your own material characteristics, processing volume, working environment, budget, and requirements for equipment accuracy and automation to obtain customized quotation plans and select the most suitable equipment.
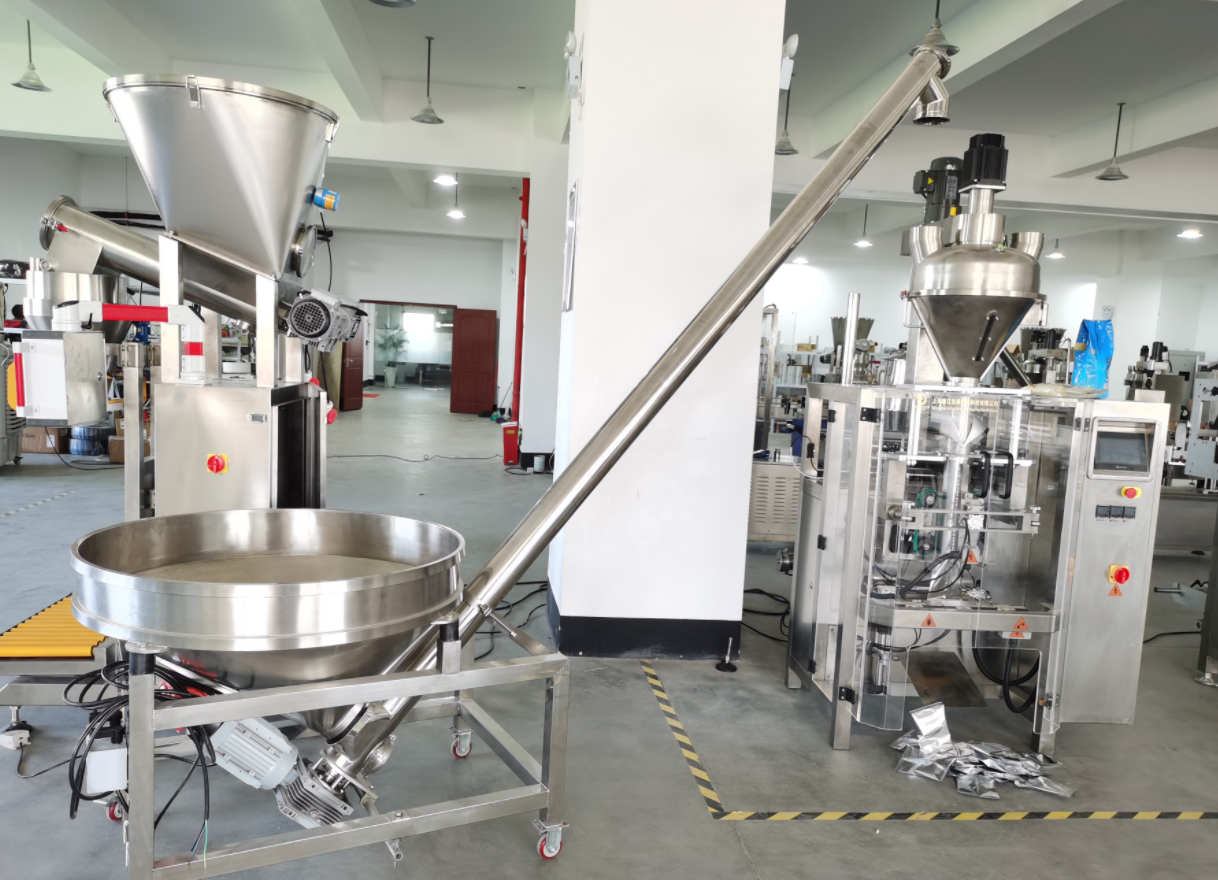

Screw Feeder can select appropriate spiral form and drive mode according to the physical properties of the material to cope with challenges such as easy arching and high viscosity. In daily maintenance, its simplified structure reduces the failure rate, and the sealed design also reduces the risk of dust spillage. Daily maintenance of the equipment, such as inspection of the wear of the spiral blades and lubrication of the bearings, is the basis for ensuring its continued stable operation. Screw Feeder not only meets the requirements of accurate, continuous and uniform feeding, but also takes into account the adaptability to complex materials, environmental friendliness and compact structure, making it an indispensable material control equipment in many industrial fields.



