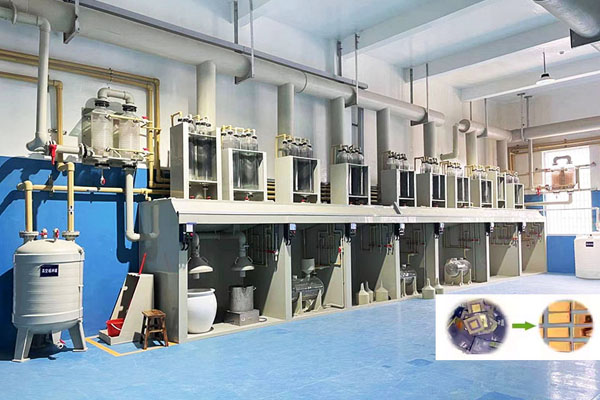
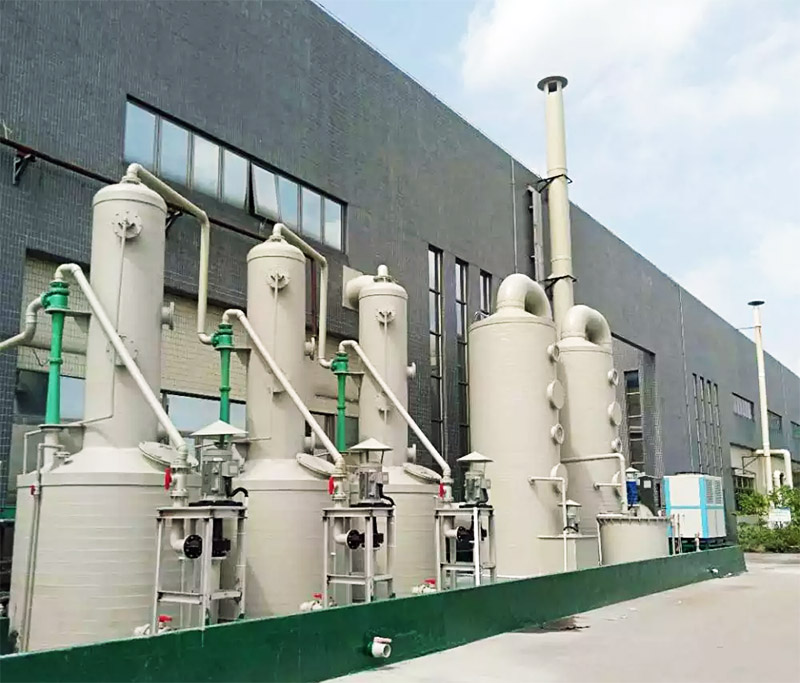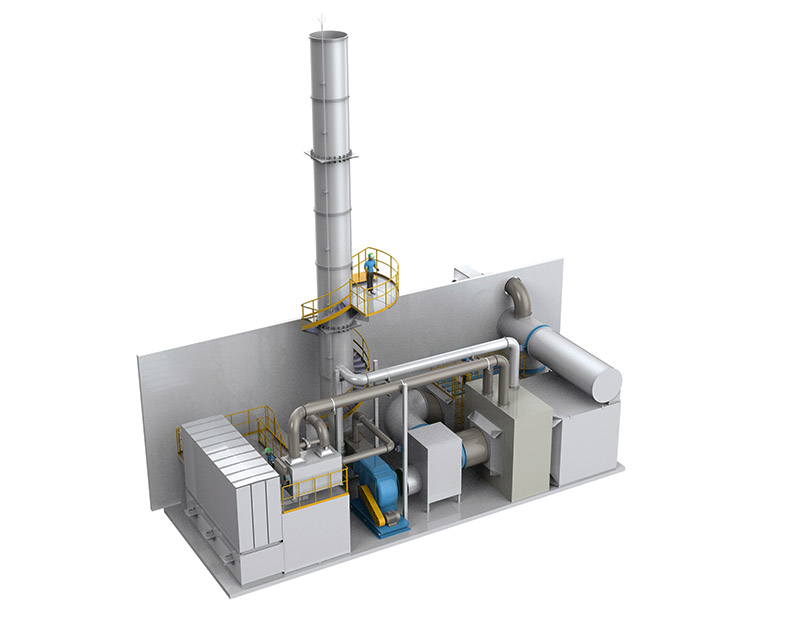
Platinum Palladium Rhodium Chemical Refining Equipment Systems
Designed for the recovery of high-purity precious metals from catalytic converters, electronic scrap and industrial by-products
Price: $500-$89,000
Reactor Material: Titanium or polypropylene
Power Consumption: Approximately 9 kW
Dimensions: Customizable based on operational needs and space constraints.
What are Platinum Palladium Rhodium Chemical Refining Equipment Systems?
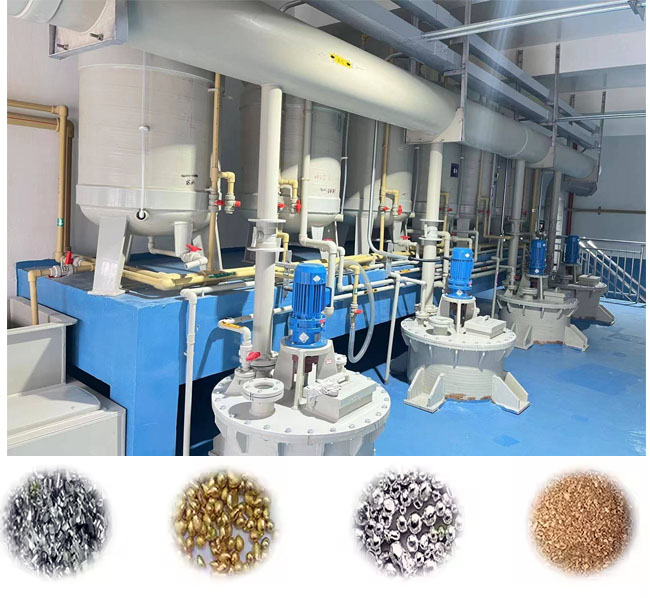

Platinum Palladium Rhodium Chemical Refining Equipment Systems are designed for the efficient recovery and purification of noble metals (PGMs) from a variety of sources, including spent catalysts, electronic waste, and jewelry scrap. Our systems utilize advanced hydrometallurgical and electrochemical refining processes to ensure purity greater than 99.95% while minimizing environmental impact.
What types of Platinum Palladium Rhodium Chemical Refining Equipment Systems are there?
Platinum Palladium Rhodium Chemical Refining Equipment Systems provides three refining systems: hydrometallurgical, electrochemical and hybrid, which are optimized for different raw materials and purity requirements to ensure fast recovery and high purity output.

Hydrometallurgical Refining Systems: It is mainly suitable for the treatment of catalytic converter waste, industrial waste and low-grade PGM raw materials. Its process includes pretreatment, dissolution, separation and purification, and reduction. This process can treat waste with complex components, and the recovery rate can reach more than 98%.
Electrochemical Refining Systems: Used for the production of high-purity platinum, palladium and rhodium (such as electronic grade and jewelry grade PGM). The process includes anode dissolution, electrolytic deposition, melting and casting, etc., which can increase the product purity to 99.99%. It is suitable for high-end applications, but the energy consumption is relatively high.
Hybrid Refining Systems: By combining the high recovery rate of the chemical method with the high purity of the electrolytic method, the overall efficiency is increased by more than 20%, and it can be used to treat high-complexity waste (such as automotive catalysts containing rhodium and ceramic carriers).
What are the advantages of Platinum Palladium Rhodium Chemical Refining Equipment Systems?
Platinum Palladium Rhodium Chemical Refining Equipment Systems can achieve high-purity recovery of precious metals and can be used for a variety of materials. It has a wide range of applications and does not pollute the environment.

High Purity Output: Achieves metal purities of up to 99.95%, suitable for high-precision applications.
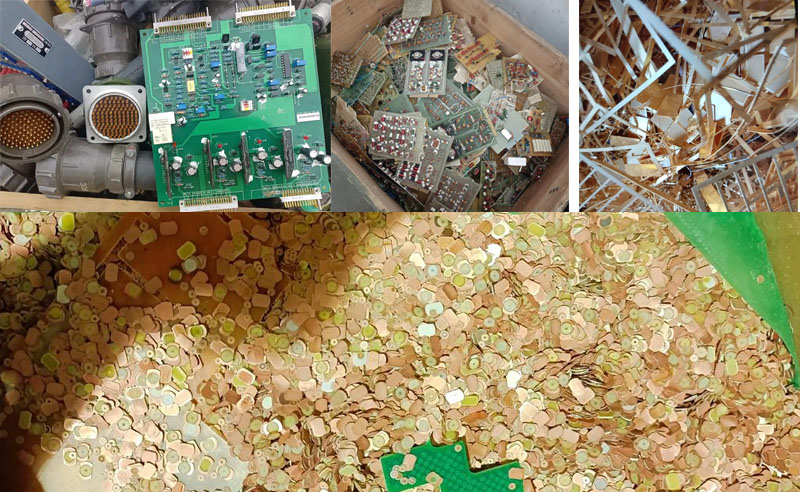
Versatility: Capable of processing various feedstocks, including spent automotive catalysts, electronic waste, and industrial residues.
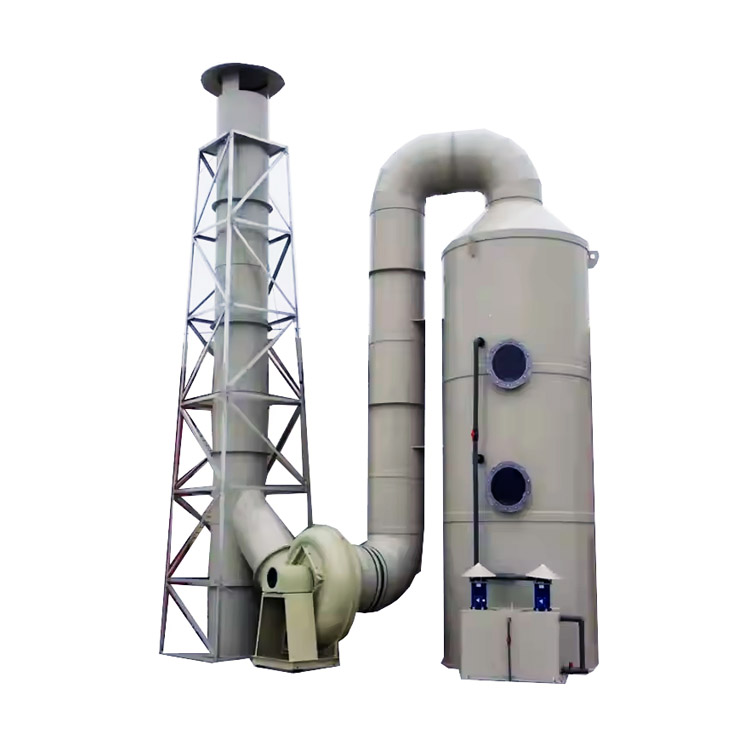
Environmental Compliance: Equipped with advanced fume scrubbers and waste treatment systems to minimize environmental impact.
Operational Efficiency: Features such as automated controls and efficient heat exchangers reduce processing time and energy consumption.
What is the Platinum Palladium Rhodium Chemical Refining Equipment Systems process?
The process flow of Platinum Palladium Rhodium Chemical Refining Equipment Systems includes the steps of Leaching, Purification, Electrolysis and Waste Treatment, as follows:
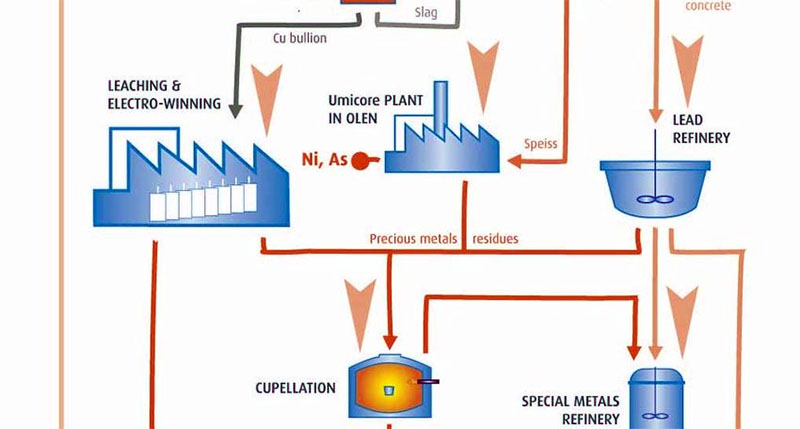
Leaching: Dissolving PGMs using aqua regia or hydrochloric acid + oxidants.
Purification: Selective precipitation, solvent extraction, or ion exchange.
Electrolysis: High-purity metal deposition via electrochemical refining.
Waste Treatment: Neutralization & recycling of residual chemicals.
Platinum Palladium Rhodium Chemical Refining Equipment Systems Parameter
| Parameter | Specification |
| Input Material | Spent catalysts, e-waste, PGM scrap |
| Output Purity | 99.95% Pt, Pd, Rh |
| Processing Capacity | 100kg–10 tons/day |
| Energy Consumption | 50–200 kWh/kg |
| Refining Method | Hydrometallurgical / Electrochemical |
| Automation Level | PLC-controlled |
What are the applications of Platinum Palladium Rhodium Chemical Refining Equipment Systems?
Automotive Industry: Recovery of PGMs from spent catalytic converters.
Electronics Recycling: Extraction of precious metals from electronic waste components.
Jewelry Manufacturing: Refining of scrap materials and production residues.
Chemical Processing: Purification of PGMs used as catalysts in various chemical reactions.




