What is the Analytic Sieve material analysis method?
Monday July-14 2025 15:29:27
What is the Analytic Sieve material analysis method?
The Analytic Sieve material analysis method is a classic technique for determining particle size distribution and classifying granular materials using standard test sieves. It separates particles of different sizes through the precise differences in sieve aperture sizes. This method, which relies on international standards such as ISO 3310 and ASTM E11, is widely used in laboratory testing and industrial production quality control. Its core involves placing samples in a stack of multiple sieves, and through mechanical vibration or manual operation, allowing materials to pass through the sieves in order of particle size. Finally, by weighing the residual materials in each sieve layer, the proportion of particle size distribution is calculated. From micron-level powders to millimeter-level particles, the Analytic Sieve method can provide reliable screening data, serving as a fundamental tool for material property research and production process optimization.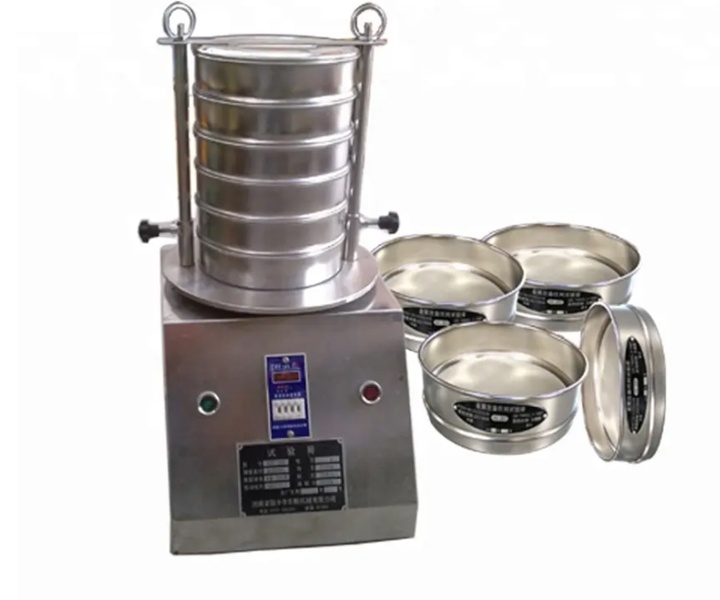
What are the specific operation methods of the Analytic Sieve material analysis?
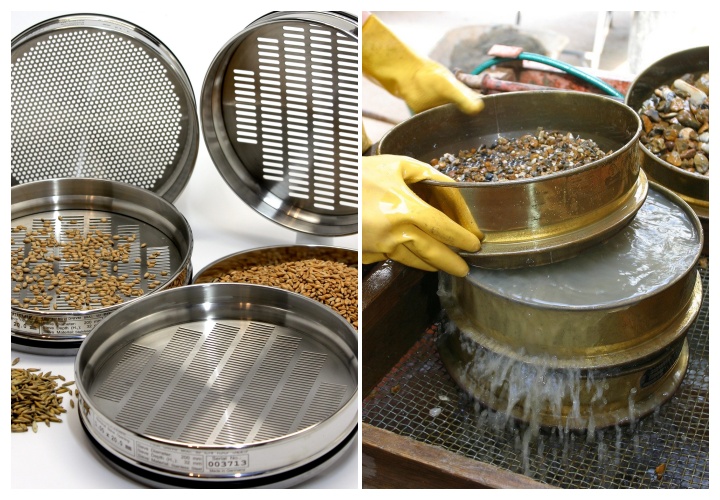

The Analytic Sieve material analysis mainly includes two operation methods: dry sieving and wet sieving, each suitable for materials with different properties.
Dry sieving: Applicable to dry, loose, and non-agglomerated materials. During operation, a fixed amount of sample is placed in the top sieve, with the vibration frequency (usually 300-500 times per minute) and time (5-15 minutes) set, and classification is completed using a mechanical sieve shaker.
Wet sieving: For moist, easy-to-cake, or viscous materials, the sample needs to be mixed with a dispersing agent (such as water or alcohol) first, then poured into a wet sieving device. Water flow is used to assist particles in passing through the sieve to avoid sieve blockage. Both methods require stacking sieves in order of decreasing aperture size. After sieving, residuals in each layer are collected, weighed, and calculated.
What are the prominent advantages of the Analytic Sieve material analysis method?
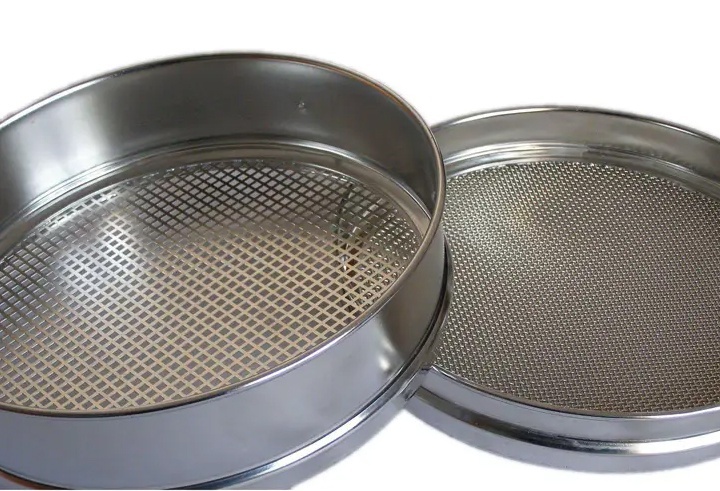

The advantages of the Analytic Sieve material analysis method lie in controllable precision, simple operation, low cost, and strong applicability.
With standardized sieve apertures (error ≤±3%), it can achieve accurate particle size classification, meeting the precision requirements of international standards such as ISO and ASTM. The operation does not require complex instruments; manual sieving or basic vibration equipment can complete the process, resulting in low training costs. The equipment is easy to maintain, as the Analytic Sieve can be reused, and the cost of a single analysis is only 1/10 of that of a laser particle size analyzer. It is also applicable to various materials such as metal powders, ores, and food raw materials, especially in the 10μm-10mm particle size range, where its data stability is better than other methods.
What is the working principle of the Analytic Sieve material analysis method?
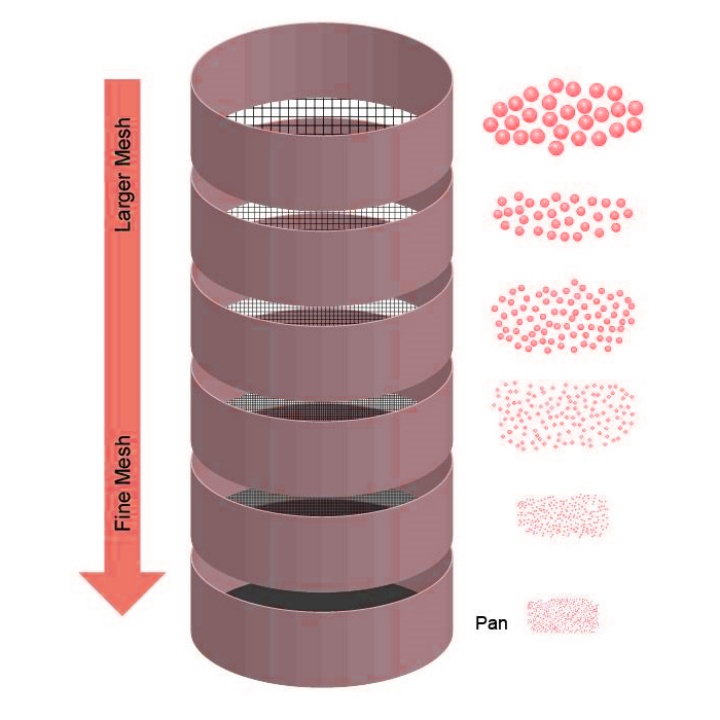
The core principle of the Analytic Sieve material analysis method is to achieve separation by matching sieve aperture sizes with particle sizes.
Multiple sieves are stacked in order of decreasing aperture size, with the top layer for sample addition and the bottom layer as a collection tray. Under external forces such as vibration and shaking, materials move on the sieve surface. Particles smaller than the sieve aperture pass through to the lower layer, while those larger than the aperture remain in the current sieve layer. By controlling sieving time (usually 5-30 minutes) and external force intensity, sufficient particle classification is ensured. Finally, based on the proportion of residual mass in each sieve layer to the total sample mass, a particle size distribution curve is drawn, intuitively reflecting the proportion of particles of different sizes in the material.
In which fields is the Analytic Sieve material analysis method applicable?

The Analytic Sieve material analysis method is widely used in fields such as mining, chemical industry, food, pharmaceuticals, and building materials.
In the mining industry, it is used for particle size detection after ore crushing to guide the adjustment of grinding process parameters.
In chemical production, it classifies powders such as catalysts and pigments to ensure product activity and uniformity. In the food industry, it controls the fineness of flour and sucrose through sieving to ensure taste and processing performance.
In the pharmaceutical field, according to pharmacopoeia standards, it detects the particle size of traditional Chinese medicine granules and western medicine powders to ensure drug release efficiency. In the building materials industry, it is used for gradation analysis of cement and sand to optimize concrete strength and fluidity.
The Analytic Sieve material analysis method, as a basic means of particle detection, its value lies in providing accurate particle size data support for production. In practical applications, it is necessary to choose dry or wet operation according to material properties, and select corresponding sieve sets in accordance with industry standards (such as pharmacopoeia sieves for pharmaceuticals, ASTM standard sieves for export products). Regular calibration of sieve apertures and standardization of operating procedures can further improve data reliability. With technological development, combining this method with automated sieving equipment can realize efficient detection of batch samples. Reasonable application of the Analytic Sieve material analysis method can effectively reduce production losses, improve product quality, and serve as an important technical bridge connecting laboratory research and industrial production.



