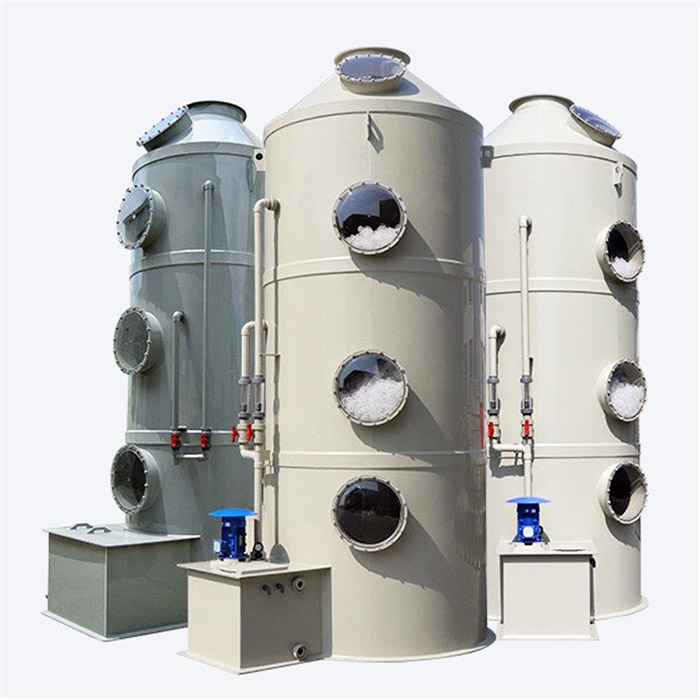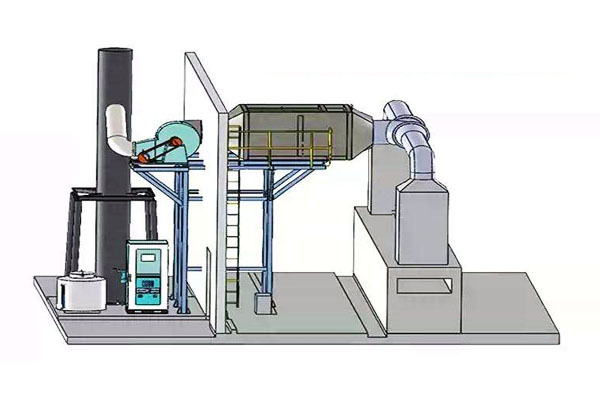
high concentration Nox Flue Waste Gas Treatment Equipment System
Mainly used to efficiently remove nitrogen oxides (NOx) from industrial emissions and reduce air pollution
Price: $550-$45,000
NOx Removal Rate: Up to 95%
Emission Output: <50mg/Nm³ (configurable to <30mg/Nm³)
Applications: Power plants, steel mills, cement factories, chemical plants, waste incinerators
What is high concentration Nox Flue Waste Gas Treatment Equipment System?
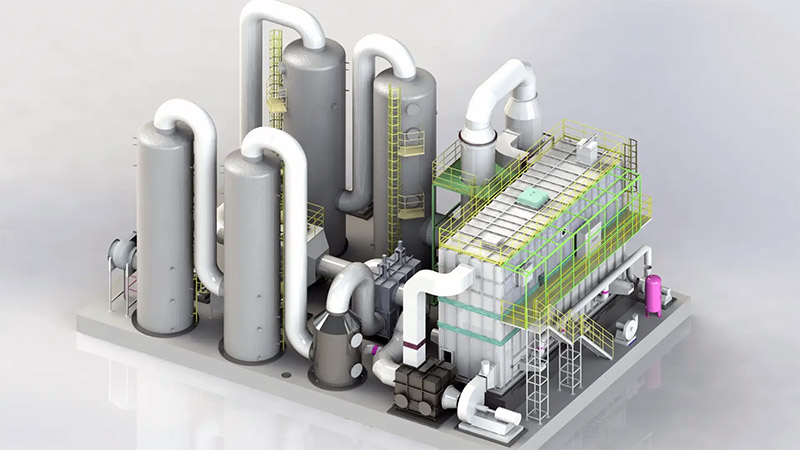
Our high concentration Nox Flue Waste Gas Treatment Equipment System is designed for industries facing stringent NOx (Nitrogen Oxides) emission regulations. Utilizing Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) and Selective Non-Catalytic Reduction (SNCR) technologies, our system ensures NOx reduction efficiency of 90%+, meeting global environmental standards such as EPA, EU Industrial Emissions Directive (IED), and China's Ultra-Low Emission (ULE) policies.
What are the advantages of high concentration Nox Flue Waste Gas Treatment Equipment System?
The high concentration Nox Flue Waste Gas Treatment Equipment System can effectively achieve a high concentration nitrogen oxide removal rate of up to 98%, extremely low ammonia escape, significant energy saving, and intelligent control to reduce costs and increase efficiency.
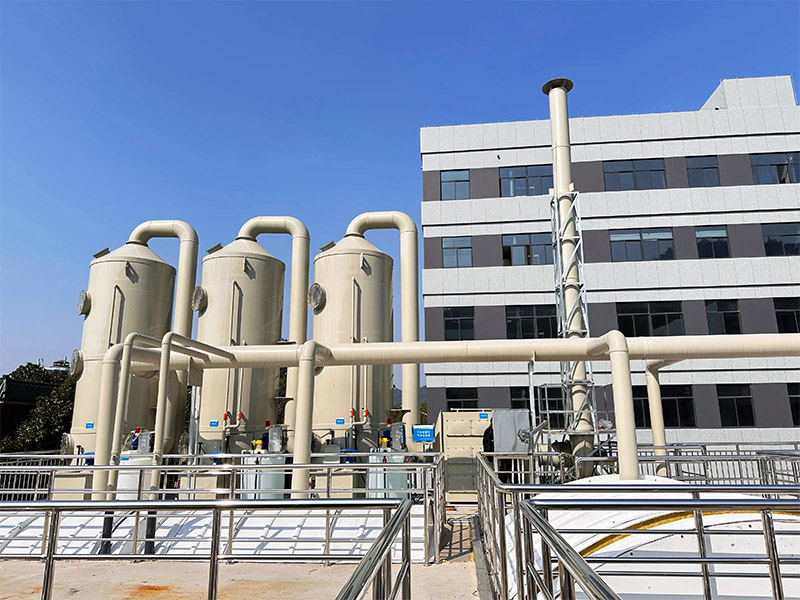

Ultra-High Efficiency: Advanced SCR/SNCR hybrid technology ensures NOx reduction rates of 90-98%, even for flue gases with NOx >1000mg/Nm³.
Low Ammonia Slip: Patented ammonia injection grid (AIG) minimizes NH₃ slip to <3ppm, reducing secondary pollution.
Energy-Efficient Design: Low-pressure drop catalyst modules reduce fan power consumption by 20%.
Modular & Scalable: Customizable for small boilers (10,000 Nm³/h) to large power plants (1,000,000+ Nm³/h).
Smart Control System: AI-based NOx prediction optimizes reagent dosing, reducing operational costs by 15%
What is the principle of high concentration Nox Flue Waste Gas Treatment Equipment System?
High concentration Nox Flue Waste Gas Treatment Equipment System adopts selective catalytic reduction (SCR) and non-catalytic reduction (SNCR) two-stage nitrogen oxide emission reduction technology:
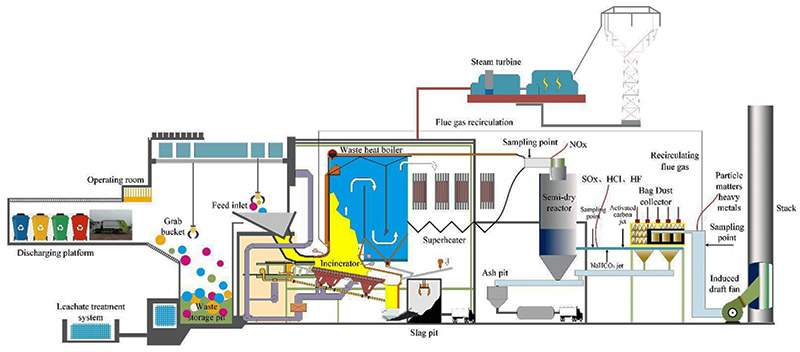
Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR): NOx + NH₃ (urea) → N₂ + H₂O (over a TiO₂/V₂O₅/WO₃ catalyst at 300-400°C).
Best for stable high-load operations (e.g., coal-fired power plants).
Selective Non-Catalytic Reduction (SNCR): NOx + NH₃ → N₂ + H₂O (at 900-1100°C without a catalyst).
Ideal for fluctuating loads (e.g., waste incinerators, cement kilns).
Hybrid Mode: Combines SCR (for baseline NOx) + SNCR (for peak loads) to maximize efficiency
High concentration Nox Flue Waste Gas Treatment Equipment System Parameters
| Parameter | Specification |
| NOx Inlet Concentration | 200-2000 mg/Nm³ |
| NOx Removal Efficiency | 90-98% |
| Outlet NOx Level | <50 mg/Nm³ (configurable to <30 mg/Nm³) |
| Operating Temperature | SCR: 300-400°C / SNCR: 900-1100°C |
| Ammonia Slip | <3 ppm |
| System Pressure Drop | <800 Pa |
| Catalyst Life | 3-5 years (replaceable) |
What are the applications of High concentration Nox Flue Waste Gas Treatment Equipment System?
High concentration Nox Flue Waste Gas Treatment Equipment System is the preferred solution for industrial waste gas purification. It is suitable for power, chemical, steel and other industries to ensure that emissions meet environmental protection standards (such as GB16297-1996). At the same time, it can recover heat energy and reduce operating costs.

Power Plants – Coal, gas, biomass boilers.
Steel & Metal Industry – Blast furnaces, sintering plants.
Cement & Lime Kilns – High-dust flue gas environments.
Chemical & Petrochemical – Nitric acid plants, refinery heaters.
Waste Incineration – Municipal & hazardous waste treatment.
High concentration Nox Flue Waste Gas Treatment Equipment System Customer Case
| Case | NOx Input (mg/Nm3) | NOx Output (mg/Nm3) | Reduction (%) | Technology | Key Outcome/Savings |
| Coal-Fired Power Plant (China) | 1200 | 45 (96% reduction). | 96 | SCR + AI-controlled urea dosing | Reduced reagent consumption by 18% |
| Steel Mill (India) | 800 | 30 | 96.3 | Hybrid SCR/SNCR system | Complied with India’s CPCB norms (2025) |



