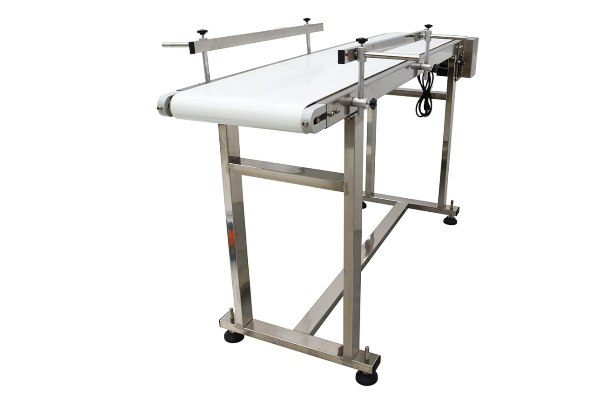
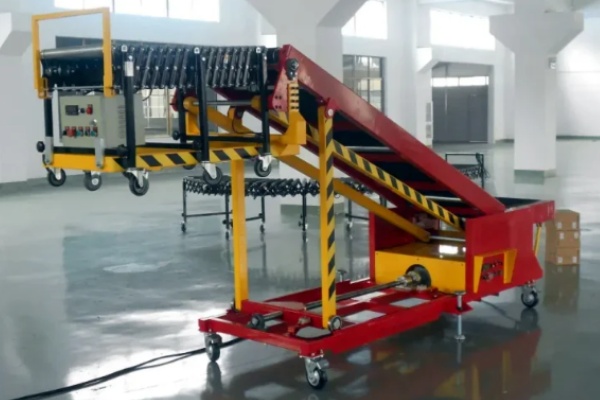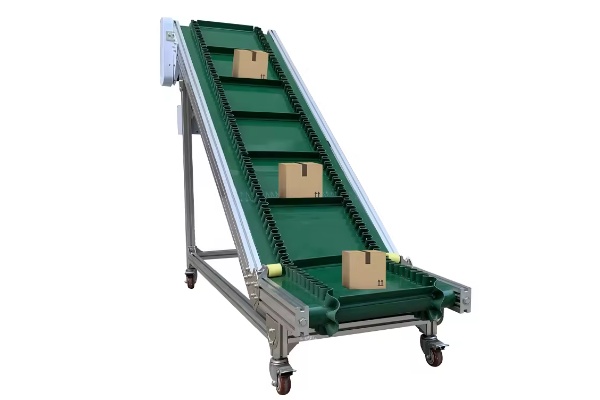
Food Grade Belt Conveyor
The price of Food Grade Belt Conveyor varies greatly depending on the belt material, conveying length, width, structure and configuration, usually ranging from US$80 to US$3,000.
Operating frequency: 50/60Hz
Width: 200/300/400/customizable
Height: 80/100/120/150 mm/customizable
Voltage: 220V, 380V
Capacity: 2-6m³/h
Hopper Volume: 0.8L/1.8L/4L/10L
What is Food Grade Belt Conveyor?
Food Grade Belt Conveyor are primarily used for continuous conveying of various food products on production lines. Based on the belt material, these conveyor belts are primarily categorized into polyurethane, polyvinyl chloride, and silicone types to accommodate different material properties and production requirements. Food-grade belt conveyors can handle capacities ranging from hundreds of kilograms to several tons per hour, with conveying distances ranging from a few meters to tens of meters, meeting the needs of various production scales.
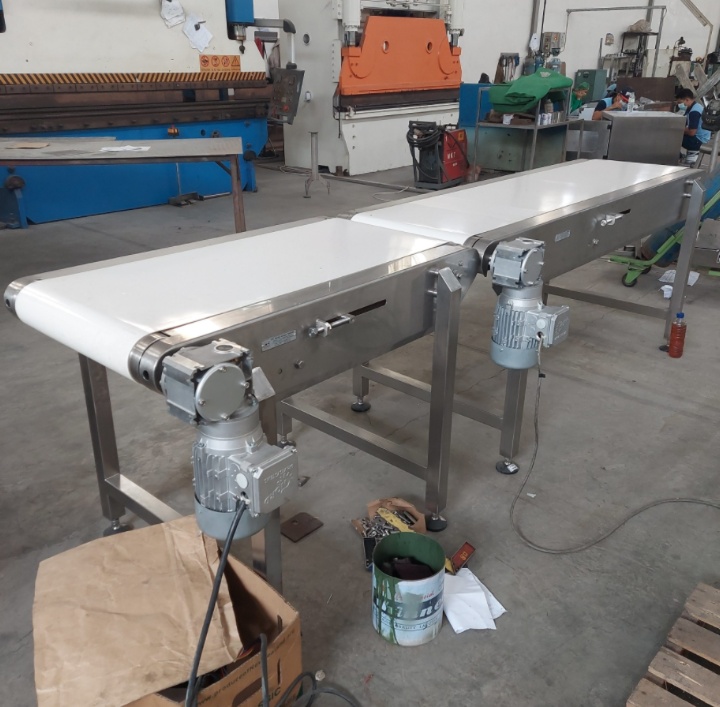

What are the types of food grade belt conveyors?
Food grade belt conveyors are primarily categorized by the belt material used. Common food-grade belt materials include polyurethane (PU), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and silicone. The following is a detailed introduction to three types:
Polyurethane (PU) Belt Conveyor
Temperature Range: PU belts typically operate stably within a temperature range of -10°C to +80°C and can withstand short periods of high temperatures.
Oil Resistance: PU belts offer excellent resistance to oils, greases, and solvents, and are not susceptible to corrosion from plant and animal fats.
Abrasion Resistance: The surface is highly abrasion-resistant, with good cut and tear resistance, resulting in a relatively long service life. Cleaning: The smooth surface makes it easy to clean and meets food hygiene standards.
Construction: Belts can be manufactured as flat, flap, or skirt belts to suit the conveying needs of different materials.
Applicable Materials: PU conveyor belts are widely used for conveying greasy foods such as meat, poultry, seafood, baked goods, chocolate, candy, and biscuits. Their excellent oil resistance makes them ideal for handling greasy, slippery foods. Furthermore, due to their wear resistance and easy cleaning properties, they are also commonly used for conveying produce such as fresh vegetables and fruit that require frequent washing.

Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Belt Conveyor
Temperature Range: PVC belts typically have a temperature range of -10°C to +60°C and are not suitable for prolonged use in high-temperature environments.
Oil Resistance: PVC belts are less oil-resistant than PU belts and are susceptible to corrosion from animal and vegetable oils. Long-term contact with oils and fats may cause the belt to harden or crack.
Abrasion Resistance: PVC belts offer some wear resistance, but their cut and tear resistance is slightly inferior to that of PU belts.
Price: Compared to PU belts, PVC belts have lower manufacturing costs and offer a more competitive price.
Structure: PVC belt conveyors can be manufactured in a variety of configurations to meet diverse material conveying requirements.
Applicable Materials: PVC belt conveyors are commonly used for conveying dry, grease-free foods such as grains, flour, rice, nuts, potato chips, and puffed foods. Due to their price advantage, PVC belts are a common choice for applications with limited budgets and less demanding belt performance.

Silicone Belt Conveyor
Temperature Range: Silicone belts offer a wide temperature range, typically from -40°C to +200°C, or even higher, and can withstand extreme high and low temperatures.
Oil Resistance: They offer excellent oil and chemical resistance and are non-toxic and odorless.
Surface: Their surface has a natural non-stick property, making them ideal for conveying sticky materials.
Flexibility: They offer excellent elasticity and flexibility, adapting to various complex conveying paths.
Cleaning: Their smooth, non-stick surface makes them very easy to clean and maintain.
Applicable Materials: Silicone belt conveyors are ideal for conveying highly sticky, hot, or frozen foods. For example, caramel, syrup, dough, freshly baked goods, frozen foods, ice cream, and more. Its high-temperature resistance also makes it commonly used in food production processes such as baking and cooling.
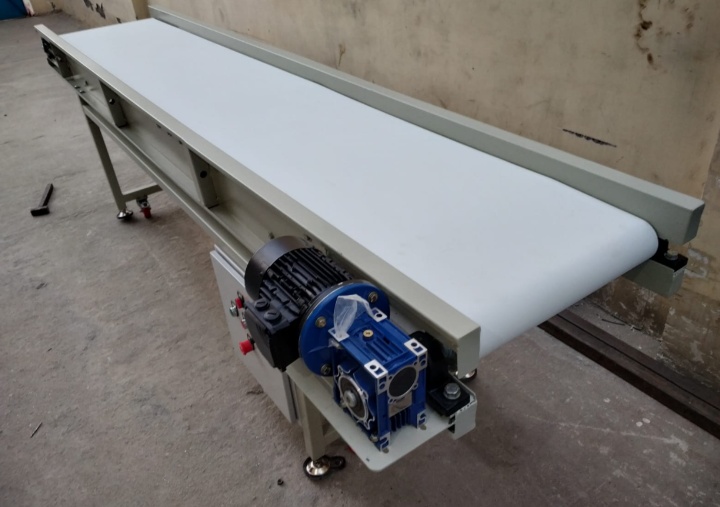

What are the advantages of a food grade belt conveyor?
Compared to conventional conveying equipment, the core advantage of a food-grade belt conveyor is its ability to ensure food safety and hygiene while meeting the specific needs of production lines. The following are its key advantages:
Ensuring food safety and hygiene: The belt materials used, such as PU, PVC, and silicone, meet standards for food contact materials. These materials are generally non-toxic and odorless (do not release harmful substances or odors, and do not contaminate the food itself), resistant to bacterial and mold growth (the belt surface is smooth and flat, not prone to harboring dirt, effectively inhibiting the growth of bacteria and mold), and easy to clean and disinfect (the belt material is resistant to water, oil, and chemical cleaning agents, allowing for high-pressure water jet cleaning and disinfection, thus meeting stringent hygiene requirements).
Adaptable to a variety of food characteristics: Foods vary greatly in physical and chemical properties. The Food Grade Belt Conveyor can be equipped with various belt materials to meet specific needs, adapting to conveying a wide range of materials. It is oil-resistant and corrosion-resistant. For high-fat foods like meat and seafood, PU belts offer excellent oil resistance, preventing belt degradation caused by grease corrosion. Silicone belts are also heat-resistant and non-sticky. The heat resistance and natural non-stick properties of silicone belts are particularly important for freshly baked goods or sticky candies. PU belts are also cut- and abrasion-resistant, effectively preventing damage from sharp objects or prolonged friction during conveying.
Improving Production Efficiency: The Food Grade Belt Conveyor significantly improves production efficiency through automated, continuous conveying. It seamlessly integrates with other equipment on the production line, such as sorting machines and packaging machines, to form a complete automated production process. Furthermore, its adjustable conveying speed allows for precise control of material delivery rhythm to meet the process requirements of different production links.
Reducing Material Loss and Cross-Contamination: Its stable belt conveyor reduces vibration and collision during conveying, thereby reducing material breakage. Furthermore, because the belt is easy to clean, it can be quickly cleaned when changing conveyed materials, effectively preventing cross-contamination between different batches or types of food.

Food Grade Belt Conveyor Parameters
|
Belt width (mm) |
Conveying length(m) Power(kw) |
Conveying speed (m/s) |
Conveying amount (t/h) |
||
| B400 | ≤10 | 12-15 | 5-30 | 1.25-2.0 | 30-60 |
| 3 | 3-4 | 4-7.5 | |||
| B500 | ≤10 | 12-15 | 15-30 | 1.25-2.0 | 40-80 |
| 3 | 4-5.5 | 5.5-7.5 | |||
| B650 | ≤10 | 12-15 | 15-30 | 1.25-2.0 | 80-120 |
| 4 | 7.5 | 7.5-11 | |||
| B800 | ≤10 | 12-15 | 15-30 | 1.25-2.0 | 120-200 |
| 4 | 7.5 | 7.5-15 | |||
| B1000 | ≤10 | 10-20 | 20-40 | 1.25-2.0 | 200-320 |
| 5.5 | 7.5-11 | 11-22 | |||
| B1200 | ≤10 | 10-20 | 20-40 | 1.25-2.0 | 290-480 |
| 7.5 | 7.5-15 | 15-30 | |||
| B1400 | ≤10 | 10-20 | <20-40 | 1.25-2.0 | 400-680 |
| 11 | 15-22 | 22-45 | |||
| B1600 | ≤10 | 10-20 | <20-50 | 1.25-2.0 | 600-1080 |
| 15 | 22-30 | 30-75 | |||
| B1800 | ≤10 | 10-20 | <20-50 | 1.0-2.0 | 200-1500 |
| 18.5 | 30-45 | 45-110 | |||
| B2000 | ≤10 | 10-20 | <20-40 | 1.0-2.0 | 1000-2000 |
| 22 | 45-55 | 55-132 | |||
| B2400 | ≤10 | 10-20 | <20-40 | 1.0-2.0 | 1500-3000 |
| 30 | 55-75 | 75-185 | |||
What is the structure of a Food Grade Belt Conveyor?
To meet the hygiene and safety requirements of the food industry, the structure of a Food Grade Belt Conveyor has been designed and optimized based on conventional belt conveyors. Its main structural components include:
Conveyor Belt: This is the core component that comes into direct contact with food. Unlike conventional belts, food-grade belts are typically made of non-toxic, odorless, and food-contact-compliant materials such as polyurethane (PU), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), or silicone. These belts have a smooth surface that resists adhesion and is wear-, oil-, and corrosion-resistant. Belt joints are typically hot-melt seamless joints to prevent dirt and facilitate cleaning.
Frame and Support Structure: The frame is the backbone of the conveyor. To facilitate cleaning and prevent bacterial growth, the frame and support components of food-grade conveyors are typically made of stainless steel, such as 304 or 316L stainless steel. Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and a smooth, easy-to-clean surface. The frame design also strives for simplicity, avoiding corners and gaps. Some frames even feature open or removable designs for easy cleaning.
Drive and Tensioning Device: The drive unit, consisting of a motor and a reducer, provides power to the belt. To meet the hygiene requirements of the food industry, the motor is typically waterproof and dustproof, and some even feature a stainless steel housing for easy high-pressure cleaning. The reducer is often oil-free or sealed to prevent lubricant leaks and contamination of food. The tensioning device adjusts the belt's tension to ensure smooth operation. Common tensioning methods include screw tensioning and weight tensioning, both of which are designed for easy cleaning.
Rollers and Idler Rollers: Rollers, including drive rollers and bend rollers, drive and redirect the belt. The rollers in food-grade conveyors are typically made of stainless steel, sometimes with a rubberized surface coating to increase friction and protect the belt. Idler rollers support the belt and prevent it from sagging during operation. To facilitate cleaning and maintenance, food-grade conveyors often avoid rollers and instead utilize a single-piece stainless steel plate or high-molecular polyethylene liner to support the belt. This reduces blind spots and reduces belt wear.
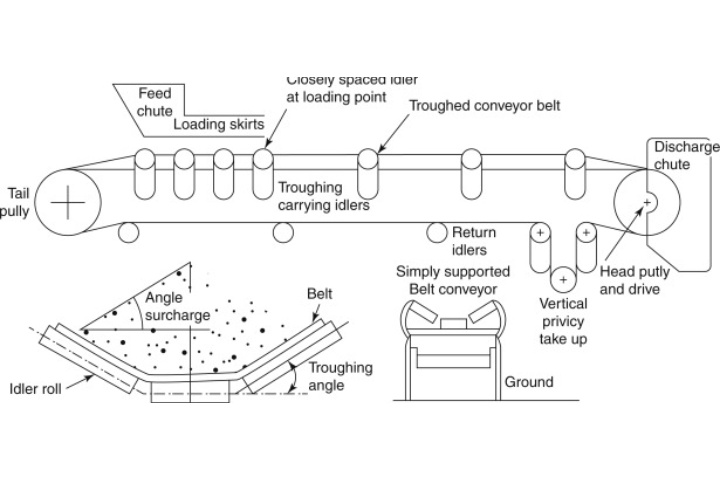
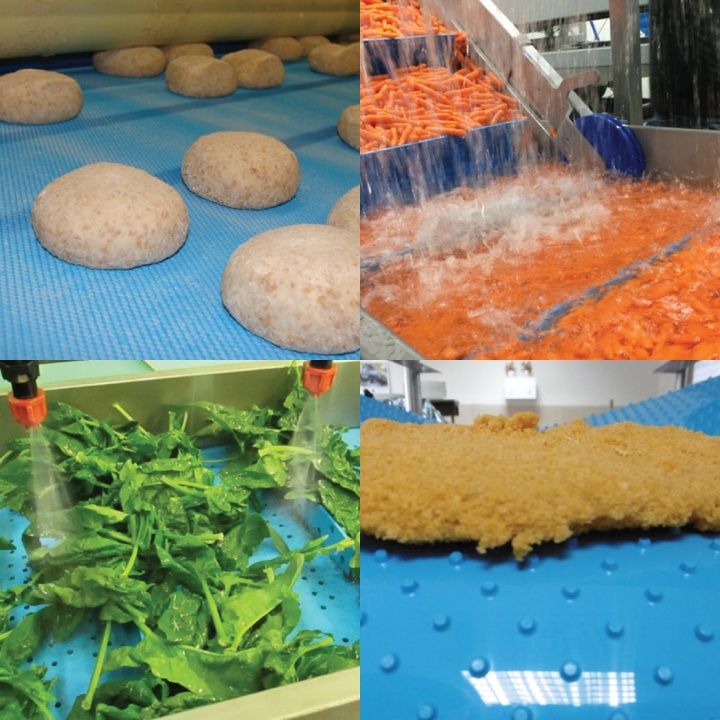
What are the Applications of Food Grade Belt Conveyors?
Due to their safety and sanitation, food grade belt conveyors are widely used in various stages of food production and processing. Their applications can be primarily categorized as follows:
Raw Material Transport and Sorting: In the early stages of food production, food grade belt conveyors are often used to transport agricultural raw materials (such as vegetables, fruits, and grains) or processed raw materials (such as flour, sugar, and condiments) from one area to another. They are also commonly used in sorting operations, such as grading fruit on an assembly line or sorting and trimming vegetables.
Processing and Handling: In food processing, conveyors are key equipment connecting different steps. For example, in meat processing, conveyors are used to transport meat for cutting and packaging; in baked goods production, conveyors are used to transport dough for forming, baking, and cooling; and in candy production, conveyors are used to transport candy for cooling, coating, and packaging.
Packaging and Cartoning: After all food processing steps are completed, conveyors transport the finished product to the packaging line. Here, the product is fed into a packaging machine for sealing and then transported to a case packer for packing. Food Grade Belt Conveyors ensure that the product remains hygienic during the final stages before packaging.
Conveying in Special Environments: In frozen food production lines, low-temperature-resistant Food Grade Belt Conveyors can be used to transport products such as ice cream and quick-frozen dumplings. In baked and fried food production, high-temperature-resistant silicone belt conveyors can be used to transport food fresh from the oven or after frying to help cool it.

The application of Food Grade Belt Conveyors in the food industry is based on their performance in meeting specific production requirements. When selecting equipment, it is important to comprehensively consider the properties of the material being conveyed, such as whether it contains oil and temperature, to determine the appropriate conveyor belt material. At the same time, the equipment's conveying capacity, distance, and ease of cleaning and maintenance are also factors that need to be weighed. By selecting a conveyor that matches the production process, you can ensure that the material conveying process meets industry standards and helps maintain stable production line operation.



