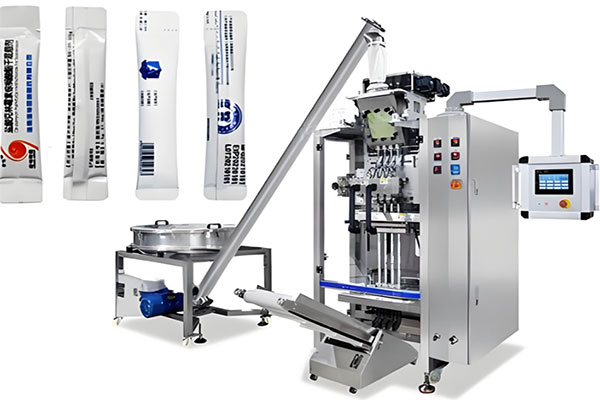
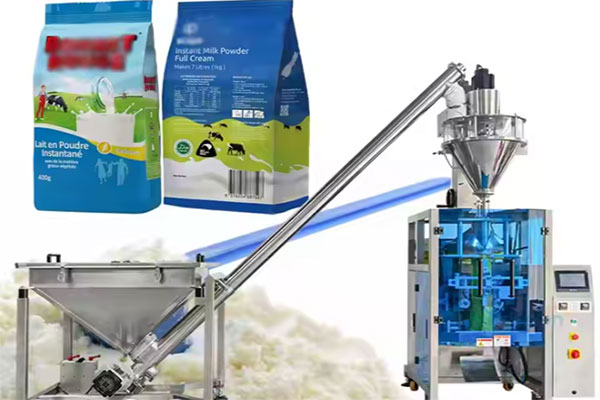
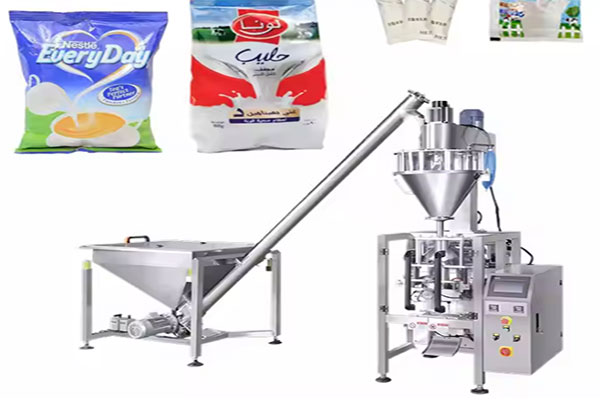
Powder Packaging Machine Process Flow
Tuesday December-09 2025 14:20:55
Powder Packaging Machine Process Flow can package dry powder materials such as protein powder, flavoring powder, and additives. The process flow typically includes elevators, raw material silos, automatic weighing scales, powder packaging machines, weight verification machines, metal detectors, inkjet printers, finished product conveyor belts, and downstream automated packing and palletizing robots, forming a series of operations from powder feeding and packaging to finished product conveying.
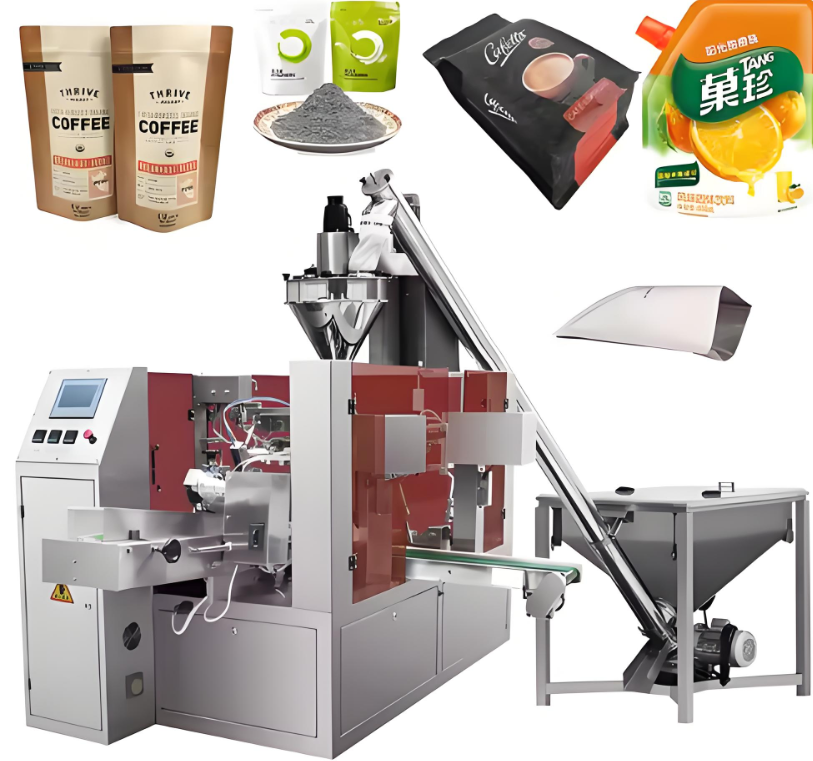

What products are included in the Powder Packaging Machine Process Flow?
The powder packaging machine process flow completes packaging through the following steps: unscrambling, feeding, augmenter dosing, filling, checking, capping, bag closing, labeling, induction sealing, sleeve filling, and final packaging. First, the scattered bottles are sorted, followed by feeding, conveying the product to the appropriate location. Then, the screw feeding method precisely controls the product filling amount for filling. After filling, the capping operation is performed. Furthermore, bag sealing, labeling, induction sealing, and sleeve labeling are performed, ultimately completing the final packaging of the product. The following is an explanation of three important powder packaging machine process flows.
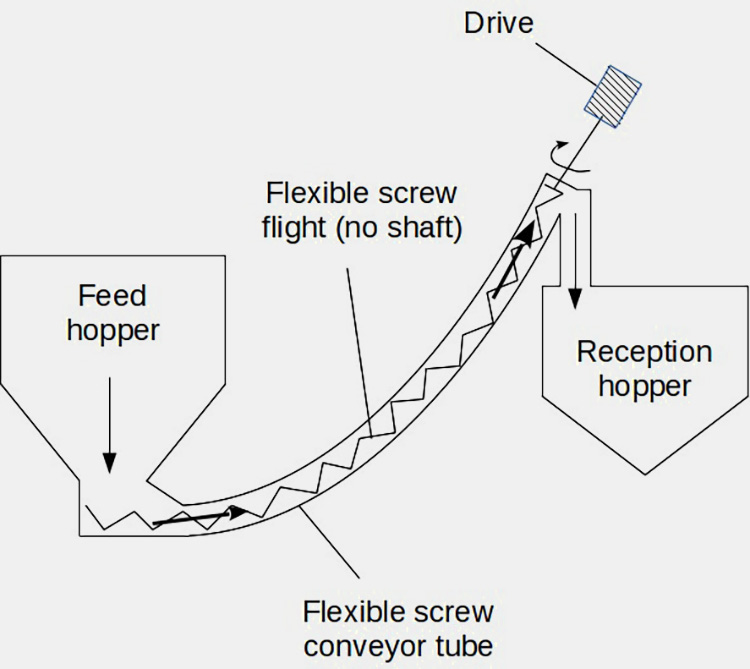
Powder Metering:A drive provides power, rotating a flexible spiral blade within a flexible spiral conveyor tube. Material enters the conveyor tube from a feed hopper. As the spiral blade rotates, the material is conveyed along the curved conveyor tube to a receiving hopper at the other end. This conveyor's flexible design makes it suitable for applications with limited space or angled conveying. Its shaftless design reduces the risk of material blockage and is particularly suitable for entangled or irregular particles.
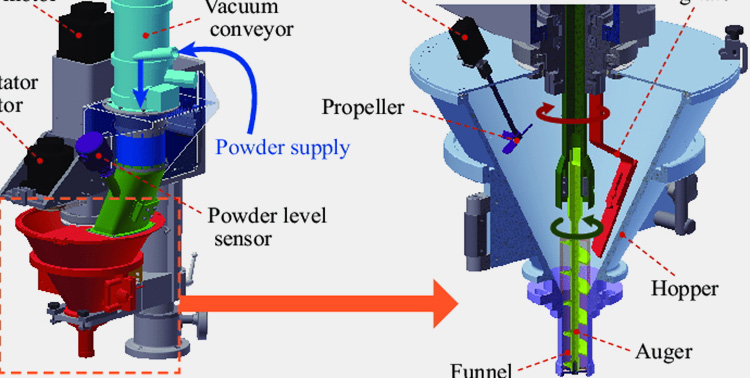
Powder Filling:The core principle of powder filling is to control the powder output per unit time through the rotation of the screw, achieving high-precision filling. The powder feeding system uses a vacuum conveyor, which uses negative pressure to transfer powder from the storage silo to the filler's hopper. A powder level sensor monitors the powder level in the hopper in real time, enabling automatic refill control. A rotator motor drives the agitator or screw to prevent powder blockage or bridging. In the core filling structure, the propeller maintains uniform powder flow within the hopper, preventing agglomeration and ensuring filling accuracy. The augmenter achieves quantitative filling through precise rotation, and the funnel accurately transfers the measured powder into the packaging bag.
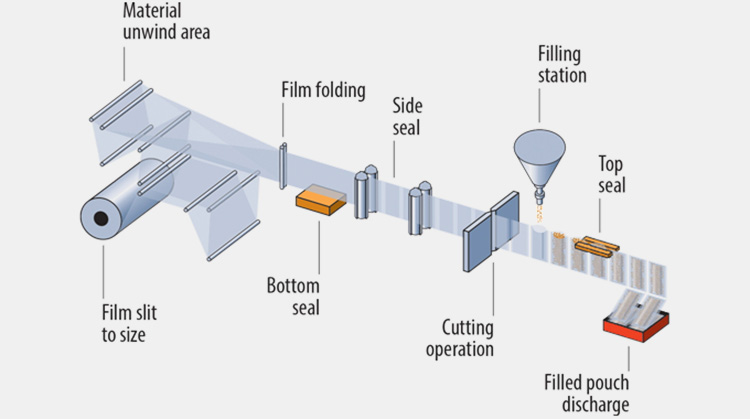
Bag Cutting:Bag cutting encompasses the entire automated process, from film roll unwinding, forming, sealing, filling, to finished product delivery. The film roll is unwound in the material unwind area, cut to size, and folded lengthwise to form the initial bag. The bottom seal and side seal are then heat-sealed to form a tubular bag, which is then cut into individual units by the cutting operation. In the filling station, the product is precisely filled into bags through a hopper, sealed with a top seal, and finally discharged by the filled pouch discharge.
Powder Packaging Machine Process Flow Selection Guide
When selecting a powder packaging machine, you can choose a single-head or multi-head packaging machine based on your production volume. When the packaging container is a bag, you can use an automatic feeder, screw metering machine, pre-packaging bag machine, automatic alignment device, metal detector, etc.; if the packaging container is a can, you can combine it with a can unscrambler, automatic filling machine, capping machine or aluminum foil sealing machine, labeling machine, etc. After packaging, the bags or cans can be coded and then transported by inclined belt conveyor or flat belt conveyor to the boxing position for packing, and then distributed to various suppliers.

How to choose a manufacturer for Powder Packaging Machine Process Flow?
When choosing a manufacturer, it's important to consider whether they offer a complete set of equipment or customized solutions. Some manufacturers produce full sets, while others only manufacture single packaging machines, which wastes the customer's time choosing complementary products. Machrise offers complete sets of machines, including flat belt conveyors, inclined screw conveyors, and powder packaging machines, to complete the entire Powder Packaging Machine Process Flow production line. They can also customize a series of machines according to specific powder packaging output requirements.
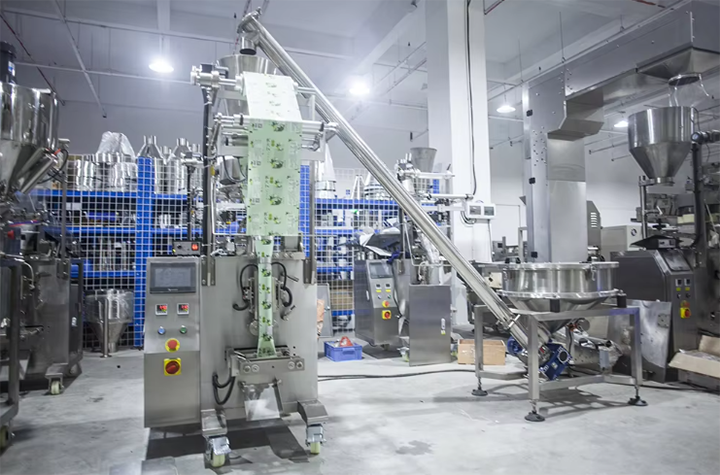

The powder packaging machine process flow encompasses the entire process from material supply to finished product output. Choosing the right packaging machine for each powder's characteristics is crucial. Powders with poor flowability require a vibration device or stirring system; dust-prone materials require a fully enclosed design; and high-precision industries require micro-metering screws or dynamic weighing technology. As technology advances, powder packaging machines will further enhance their automation and adaptability, providing businesses with more efficient packaging solutions.



